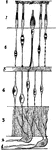The Human Sensory Systems: Sight ClipArt gallery offers 189 illustrations related to human vision.
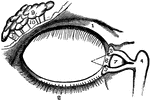
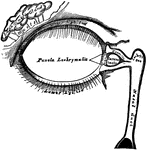
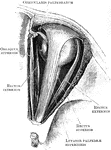
Lachrymal Apparatus
The lachrymal apparatus (the skin of the lids has been removed), which functions in tear production.
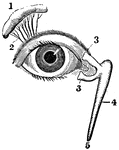
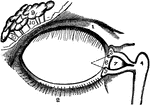
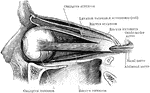
View of the Lachrymal Gland and Nasal Duct
View of the lachrymal gland and nasal duct. Labels: 1, The lachrymal gland. 2, Ducts leading from the…
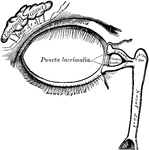
Lacrimal Apparatus
The lacrimal apparatus consists of the lacrimal gland, which secretes the tears, and its excretory ducts,…
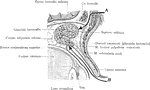
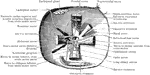
Lacrimal Gland
The two portions of the lacrimal gland, as seen in a lateral sagittal section of the orbit. A: Mode…
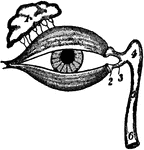
The Lacrimal Gland
The lacrimal (lachrymal) gland is an oval gland in the orbital portion of the frontal bone. Its tear…
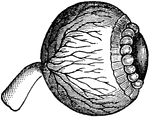
Lens of the Eye
The crystalline lens, which is a bi-convex, elastic, transparent body, enclosed in a capsule, held in…
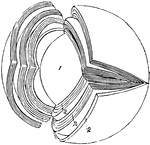
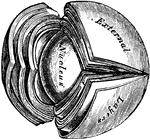
Crystalline Lens
Laminated structure of the crystalline lens. The laminae are split up after hardening in alcohol. Labels:…
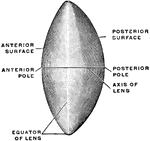
Section Through Lens
Section through the equator of the lens. Showing gradual transition of the epithelium into lens fibers.
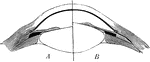
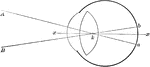
The Use of the Crystalline Lens
A convex lens, bends the ray of light which pass through it, so that they meet at a point called a focus.…
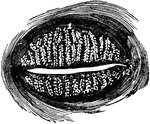
Meibomian Glands
Meibomian glands (glandulae tarsales), which are sebaceous glands embedded in grooves in the inner surface…

Eyelid, Muscles of
Muscles of the eyelids, the elevator passing back into the orbit; the sphincter, or orbicular muscle…
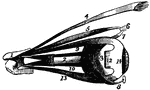
Eye Muscles
The muscles of the eyeball, the view being taken from the outer side of the right orbit.
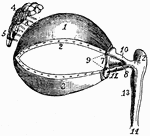
Eye Muscles
1, cartilage of the upper eyelid; 2, its lower border, showing the openings of the Meibomian glands;…
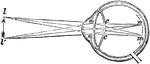
Near-sighted
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed in the eye of a near-sighted person. The…

Nearsighted Vision
The lenses and humors of the eye must be very exactly arranged, in order that the sight may be perfect.…
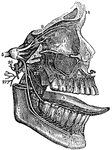
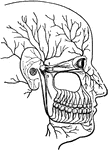
The Fifth Pair of Nerves
A distribution of the fifth pair of nerves. Labels: 1, The orbit for the eye. 2, The upper jaw. 3, The…
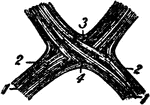
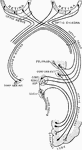
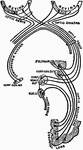
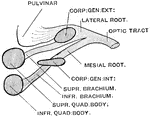
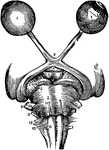
The Optic Chiasma
The optic chiasma or commissure, which is seen at the base of the brain in front of the tuber cinereum…

Optic Nerve
The terminal portion of the optic nerve and its entrance into the eyeball, in horizontal section.
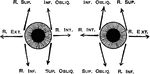
Diagram to Show the Action of the Orbital Muscle
Diagram to show the action of the orbital muscle. The arrows show the direction of the action of each…
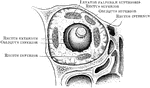
Arrangement of Orbital Muscles
Transverse vertical section through the orbit behind the eyeball to show the arrangement of muscles.
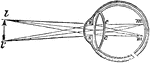
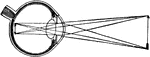
Perfect Eye
"A representation of the manner in which the image is formed upon the retina in the perfect eye. The…
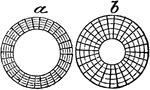
Pupil Contraction and Dilation
On the left (a) the pupil is wide open (dilated), while on the right (b) the pupil is contracted. The…

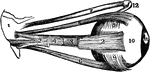
Attachment of the recti
"Showing the attachment of the recti, or straight muscles to the eyeball, also the distribution of arteries…
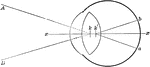
Retina
"Diagram illustrating the points at which incident rays meet the retina. xx, optic axis; k, first nodal…
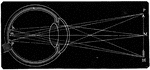
A Diagram of the Retina and Crystalline Lens
A diagram showing how an image is formed upon the retina by the crystalline lens.
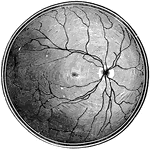
Retina Blind Spot
The right retina as it would be seen if the front part of the eyeball with the lens and vitreous humor…
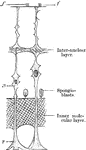
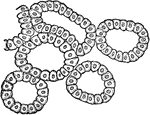
Sustentacular Fibers of the Retina Fiber Basket
Diagram showing the sustentacular fibers of the retina fiber basket above the external lumbar membrane;…
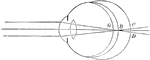
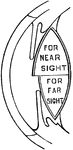
The Position of the Retina in Near and Far Sight
A flattened shape of the globe of the eye causes farsightedness and an elongated shape of the globe…
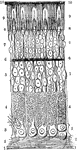
Section of Retina
A section through the retina from it anterior inner surface (1) in contact with the hyaloid membrane,…
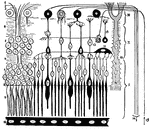
Eye Retina
Diagram of the retina, aka percipient layer of the eye. 1: inner limiting membrane, which is next to…

Layers of the Retina
Section through the macula lutea and fovea centralis of the human retina. Labels: a, fovea; b, descent…
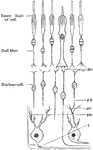
Nervous Elements of the Retina
Diagram showing the nervous elements of retina. Labels: 1, nerve fiber to ganglion cell; 2, processes…
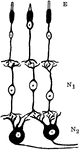
Neurons and Sensory Epithelium in the Retina
Diagram showing relations of the neurons and sensory epithelium in the retina. labels: E, epithelial…
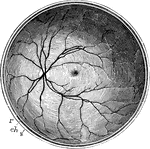
Posterior Half of the Retina
The posterior half of the retina of the left eye, viewed from before; s, the cut edge of the sclerotic…
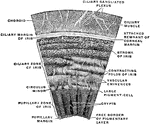
The Structure of the Retina
Next to the choroid and comprising about 1/4 the entire thickness of the retina is a multitude of transparent,…
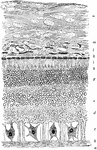
Structure of the Retina
A section of the retina, choroid, and part of the sclerotic. Labels: a, membrana limitans interna; b,…