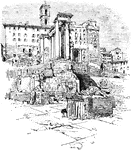This ClipArt gallery offers 249 illustrations of ancient Roman architecture. Roman architecture adopted many styles from the Greek, and is most noted for their expert implementation and frequent use of the arch and dome. See also the Roman Ornament ClipArt gallery.
Pons Cestius
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
Pons Trajan
"A bridge. As the rivers of Greece were small, and the use of the arch known to them only to a limited…
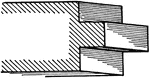
Raised Fillet
A roman moulding, called Raised Fillet. Its projection is generally made equal to its height.…

Roman Amphitheatre at Arles
The Arles Amphitheatre is a Roman amphitheatre in the southern French town of Arles.

A Roman Aqueduct
"The Pont du Gard near Nimes (ancient Nemausus) in southern France. Built by the emperor Antoninus Pius.…

Roman Bath
"Roman Bath, from a Painting on the Walls of the Thermae of Titus at Rome." — Chambers' Encyclopedia,…

Roman Baths
"The baths of Titus, the name of each part of the building is inscribed on it. The small dome inscribed…

Roman Forum in 1885
An illustration of the Roman Forum as in 1885. The Roman Forum, sometimes known by its original Latin…

A Roman Temple
"The best preserved of Roman temples. Located at Nimes in southern France, where it is known as La Maison…

The Pantheon at Rome
The pantheon at Rome is a temple that was built to all the gods of Ancient Rome. It was built by Marcus…

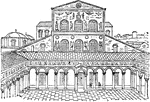
Interior of San Clemente
"San Clemente is an excellent example of the primitive church. The side enterance generally used is…

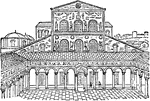
Santa Maria Maggiore
Santa Maria Maggiore church in Rome built shortly after the time of Constantine.

Sarcophagus of Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus
An illustration of the sarcophagus of Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus. Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus…
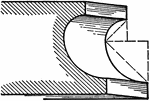
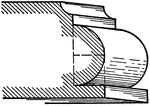
Scotia
A roman moulding, called a Scotia. It consists of two quarter circles one of which has a radius…

A Section of Hadrian's Wall in Britain
A small portion of the great, Roman-built Hadrian's Wall in Britain, begun in AD 122. Two men, one sitting…
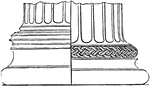
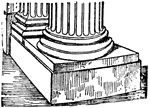
Spira
"Spira, the base of a column. in the Tuscan and the Roman Doric the base consisted of a single torus,…

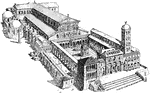
St. John's Church, Lateran Palace, Rome
The Basilica of St. John Lateran (Italian: Basilica di San Giovanni in Laterano) is the cathedral of…

Stadium
"A Greek measure of length, and the chief one used for itinerary distances. It was equal to 600 Greek…

Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix
A sculpture of the head of Lucius Cornelius Sulla. Lucius Felix. Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix, or simply…

Temple of Theseus
The Temple of Hephaestus and Athena Ergane, also known as the Hephaisteion or Theseion, is the best…
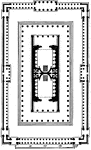
Temple of Venus and Roma, Plan
The Temple of Venus and Roma (Latin: Templum Veneris et Romae) was the largest known temple in Ancient…

Temple of Vesta, Tivoli
The circular so-called "Temple of Vesta" at Tivoli, of the early first century BCE, has been widely…

The Interior (Atrium and Peristylium) of Pansa's house at Pompeii, Restored
Illustration of a restored atrium and peristylium of the House of Pansa at Pompeii. The impluvium, pool,…
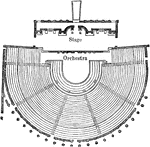
Ground Plan of the Theatre at Pompeii
"The theatre was essentially like the Grecian in its arrangement; it formed a semicircle with seats…
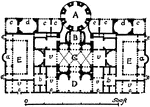
Thermæ of Caracalla, Plan of Central Block
The Baths of Caracalla were Roman public baths, or thermæ, built in Rome between AD 212 and 216,…
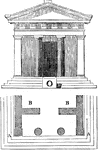
Threshold
"The threshold was, with the ancients, an object of superstitious reverence, and it was thought unfortunate…
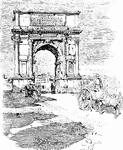
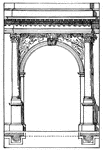
Arch of Titus
"In the time of Trajan, the Arch of titus and the Colossus of Nero (a gilt bronze statue 120 feet high),…

Roman Sarcophagus Tomb
A coffin or tomb of stone; a kind of stone chest, generally more or less ornamented for receiving a…

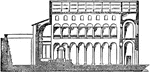
Interior of Trajan's Bascilica
"Interior view of Trajan's Basilica, as restored by Canina." — Encyclopediia Britannica, 1910