Clipart tagged: ‘"alimentary canal"’
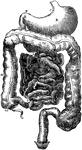
Alimentary Canal
Diagram of the abdominal part of the alimentary canal (digestive system). Labels: C, the cardiac, and…
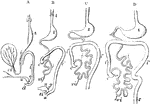
Development of the Alimentary Canal
Outlines of the form and position of the alimentary canal in successive stages of its development. A,…
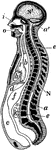
Longitudinal Section of Body
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the body. Labels: a, the neural tube, with its upper enlargement…
Development of the Intestinal Canal
Two diagrams to illustrate the development of the intestinal canal. The figure to the right shows the…
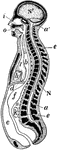
Longitudinal Section of the Body
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the Body. Labels: a, the neural tube, with its upper enlargement…
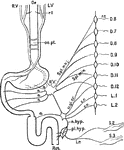
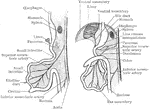
Nerves of the Alimentary Canal
Diagrammatic representation of the nerves of the alimentary canal. Oe to Rct, the various parts of the…
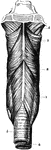
The Pharynx
The structure of the pharynx, a conical, musculo-membranous tube that forms the alimentary canal which…
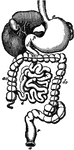
The Small Intestine
The small intestine, a convoluted, tubular, digestive organ, about 20 ft in length, extending from the…
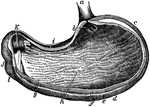
The Stomach
The stomach, the principal organ of digestion. It is a dilated part of the alimentary canal, situated…
