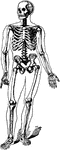
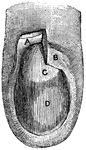
Humerus
"The humerus, a long, hollow bone, rests against a shallow socket on the shoulder blade. It…
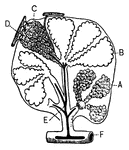
Section of a hydra
"Longitudinal section of a Hydra; b, bud which will form a young one; ba, base by…
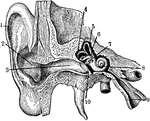
Inner Ear
1. Helix 2. Concha 3. Outer passage 4,5,6. emicircular canals 7. Oval indow 8. Cochlea 9. Eustachian…
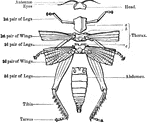
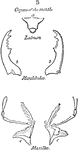
External Anatomy of an Insect Skeleton
"Anatomy of the external skeleton of an insect" — Goodrich, 1859

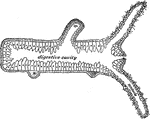
Digestive Apparatus of an Insect
"a, head, antennae, &c; b, pharynx; c, crop; d, gizzard; e, chyle-forming stomach; f, biliary vessels;…
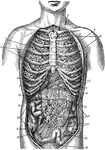
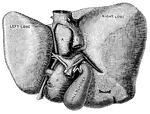
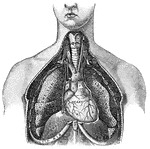
Internal Anatomy
1. Collar bone 2. Left Lung 3. Breast Bone 4. Right Lung 5. Ribs 6. Right lobe of the liver 7. Left…
Spindle Cell of Involuntary Muscle
"The involuntary muscles consist of ribbon-shaped bands which surround hollow tubes or cavities…
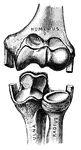
Elbow Joint
"Showing how the Ends of the Bones are shaped to form the Elbow Joint. The cut ends of a few ligaments…
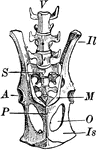
Kangaroo Pelvis
An illustration of a kangaroo pelvis. "M, marsupial bones, borne upon P, pubis; Il, ilium; Is, ischium;…
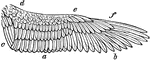
Right Wing of Kestrel
"Right wing of the Kestrel, drawn from the specimen, while being held against the light."—Pettigrew,…
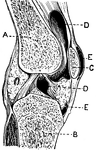
Section of the Knee
This illustration shows a section on the knee (A, Femur; B, Tibia; C, Patella; D, Synovial sac; E, bursæ).…

Northern Lapwing
"The Lapwing with one wing fully extended, and forming a long lever; the other being in a flexed condition…
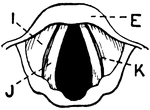
Vertical Section of Larynx
This illustration shows a vertical section of the larynx and its many parts (A. Thyroid Cartilage; B.…
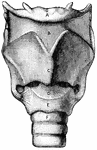
Front view of the larynx
"Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx. (Front view.) A, hyoid bone; B, membrane…
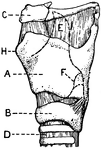
Lateral Aspect of Larynx
This illustration shows a lateral aspect of the larynx and its multiple parts (A. Thyroid Cartilage;…
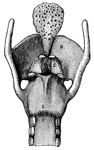
Posterior view of the larynx
"Cartilages and Ligaments of the Larynx. (Front view.) A, epiglottis; B, thyroid cartilage;…
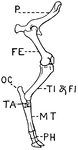
Leg of Ox
This illustration shows the leg of an Ox. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus, MT.…
Muscles of the leg
"Muscles of the leg showing how they pass into tendons at the ankle." —Davison, 1910
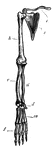
Chimp Limb
The forelimb of chimpanzee. (c) collar bone; (s) shoulder blade; (h) humerus; (r) radius; (u) ulna;…
Chimp Limb
The hindlimb of chimpanzee. (i) innominate bone; (f) thigh bone; (t) tibia; (s) fibula; (r) bones of…
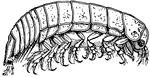
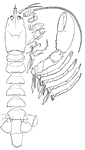
Limnoria Lignorum (Flabellifera)
Flabellifera are a tribe of isopods. Their bodies end in a tail fan, made by the last pair of appendages…
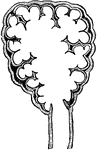
Pulmonary lobule
"Section of a pulmonary lobule, showing its division into pulmonary vesicles." — Tracy, 1888
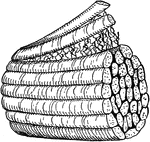
Cross-section from a shaft of a long bone
"Little openings (Haversian canals) are seen, and around them are arranged rings of bone with little…

Lungfish
In the lungfish, the development of the air bladder as a lung is much more complete than others in the…
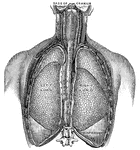
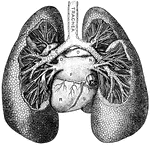
Lungs
"Relative Postion of the Lungs, the Heart, and Some of the Great Vessels belonging to the latter. A,…
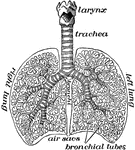
The lungs
"The lungs fill up most of the cavity of the chest. One lies on either side of the heart which is in…
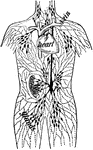
Lymph Vessels
"The lymph vessels of the body. rc, the thoracic duct; lac, the lacteals taking the lymph and fatty…
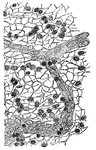
Connective Tissue from a Lymphatic Gland
"Consisting of a very fine network of fibrils, around which are cells of various sizes." — Blaisedell,…
Mackerel
The perch is typical of a large group of fishes, all of which have spiny rays. The perch is widely distributed…
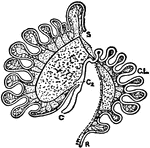
Intestinal Tract of Macropus Bennetti
S, cut end of duodenum; R, cut end of rectum; C, caecum; C2, accessory caecum; C.L., colic loop of hind-gut.

Megatherium Skeleton
Megatherium ("Great Beast") was a genus of elephant-sized ground sloths that lived from two million…

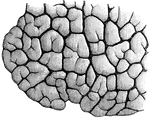
Compound microscope
"A Compound Microscope. The appearance of the various structures and tissues of the human body as revealed…
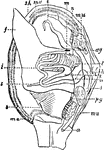
Mollusc Anatomy
"Anatomy of an Acephalous Mollusc (Mactra): s, stomach; ii, intestine; ag, anterior ganglions; pg, posterior…
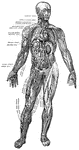
Muscles and Blood Vessels
"Principal Muscles on the Right, Certain Organs of the Chest and Abdomen, and the Larger Blood Vessels…
Muscles of the forearm
"The extensor muscles on the back of the forearm. Note the tendons at the wrist." —Davison, 1910
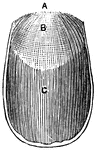
Surface of a nail
"Concave or Adherent Surface of the Nail. A, border of the root; B, whitish portion…
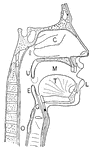
Nasal and throat passageways
"Diagram of a Sectional View of Nasal and Throat Passageways. C, nasal cavities; T,…

Nasal cavities
"Nasal Cavities, seen from Below. The sense of smell is located in the membrane which lines the cavities…
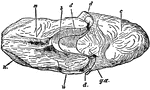
Female Nautilus without Shell
An illustration of a female nautilus without the shell. "m, The dorsal "hood" formed by the enlargement…
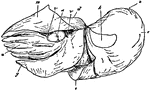
Female Nautilus without Shell
An illustration of a female nautilus without the shell. "c, points to the concave margin of the mantle-skirt…
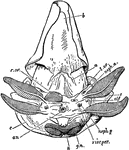
Female Nautilus without Shell
An illustration of the postero-ventral view female nautilus without the shell. "a, Muscular band passing…
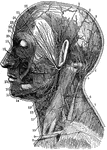
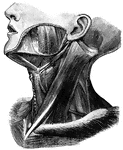
Neck
1. Temporal Artery 2. Artery behind the ear 3. Occipital Artery 4. Greater occipital nerve 5. Smaller…