Clipart tagged: ‘birds egg’
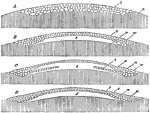
Egg Germination
"Further development of hen's egg; after Haeckel: A, the mulberry mass of cleavage cells, b, same as…
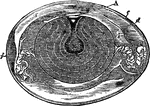
Hen's Egg
" Fig 110 - Hens egg, nat. size, in section; from Owen, after A. Thompson. A, cicatricle or "tread,"…