Clipart tagged: ‘blastoderm’
Blastoderm of a Chick
Vertical section of blastoderm of chick (1st day of incubation). S, epiblast consisting of short columnar…
Blastoderm of an Egg
Vertical section of area pellucida and area opaca (left extremity of figure) of blastoderm of a fresh…
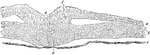
Cells of an Embryo Chick
A transverse section through an embryo chick (26 hours). Labels: a, epiblast; b, mesoblast; c, hypoblast;…
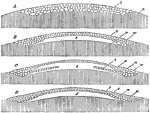
Egg Germination
"Further development of hen's egg; after Haeckel: A, the mulberry mass of cleavage cells, b, same as…