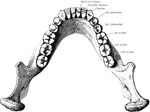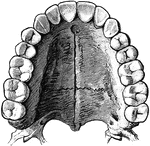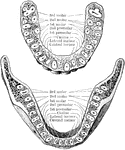
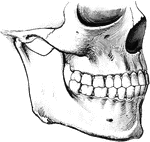
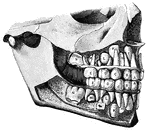
Jaw Showing Roots of Teeth
Horizontal section through both the upper and lower jaws to show the roots of the teeth. The sections…
Pug Dog
The pug is a breed of small, short-haired lap dogs, probably of Oriental origin, and introduced into…
Smooth-coated Fox-terrier
The Fox-terrier is not an old breed, only dating back about a century; but the fox-terrier's cleverness,…
Teeth
To show the relation of the upper to the lower teeth when the mouth is closed. The manner in which a…
!["A Tooth is one of the hard bodies of the mouth, attached to the skeleton, but not forming part of it and developed from the dermis or true skin. True teeth consist of one, two, or more tissues differing in their chemical composition and in their microscopical appearances. Dentine, which forms the body of the tooth, and 'cement,' which forms its outer crust, are always present, the third tissue, the 'enamel,' when present, being situated between the dentine and cement. The incisors, or cutting teeth, are situated in front. In men there are two of these incisors in each side of each jaw. The permanent incisors, molars, and premolars are preceded by a set of deciduous or milk teeth, which are lost before maturity, and replaced by the permanent ones. The canines come next to the incisors. In man there is one canine tooth in each half-jaw. The premolars (known also as bicuspids and false molars) come next in order to the canines. In man there are two premolars in each half-jaw. The true molars (or multicuspids) are placed most posteriorly. In man there are three molars in each half-jaw, the posterior one being termed the wisdom tooth. The figures [in the illustration] refer to months after birth."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15200/15256/teeth1_15256_mth.gif)
First Teeth
"A Tooth is one of the hard bodies of the mouth, attached to the skeleton, but not forming part of it…
Incisor and Canine Horse Teeth
Incisor and canine teeth of a horse. A, front, B, lateral, and C, corner incisor; D, canine teeth.
Permanent Teeth
The permanent teeth of the right side, outer or labial aspect. The upper row shows the upper teeth,…
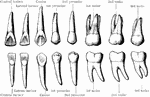
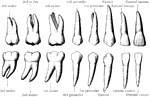
Permanent Teeth
The permanent teeth of the right side, inner of lingual aspect. The upper row shows the upper teeth,…
!["A Tooth is one of the hard bodies of the mouth, attached to the skeleton, but not forming part of it and developed from the dermis or true skin. True teeth consist of one, two, or more tissues differing in their chemical composition and in their microscopical appearances. Dentine, which forms the body of the tooth, and 'cement,' which forms its outer crust, are always present, the third tissue, the 'enamel,' when present, being situated between the dentine and cement. The incisors, or cutting teeth, are situated in front. In men there are two of these incisors in each side of each jaw. The permanent incisors, molars, and premolars are preceded by a set of deciduous or milk teeth, which are lost before maturity, and replaced by the permanent ones. The canines come next to the incisors. In man there is one canine tooth in each half-jaw. The premolars (known also as bicuspids and false molars) come next in order to the canines. In man there are two premolars in each half-jaw. The true molars (or multicuspids) are placed most posteriorly. In man there are three molars in each half-jaw, the posterior one being termed the wisdom tooth. The figures [in the illustration] refer to years after birth."—(Charles Leonard-Stuart, 1911)](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/15200/15257/teeth2_15257_mth.gif)
Second Teeth
"A Tooth is one of the hard bodies of the mouth, attached to the skeleton, but not forming part of it…
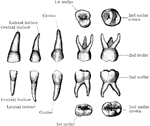
Temporary Teeth
The temporary teeth of the left side. The masticating surfaces of the tow upper molars are shown above.…
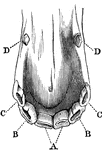
Temporary and permanent teeth
"Temporary Teeth: A, central incisors; B, lateral incisors; C, canines;…
Development of a Tooth
Diagram to illustrate the development of a tooth. I. Shows the downgrowth of the dental lamina D.L.…

Turnspit
A unique breed of greyhound. Humble but intelligent, the turnspit, which, despite its vulgarity, appears…

Wolf
The wolf belongs to the dog family. There are three recognized species of wolf and they are generally…

Wolf
"Wolf is the vernacular name of certain species of the genus Canis. The common wolf (C. lupus) has very…

American Wolf
"The common wolf is of the size of a large dog; its usual color is a yelowish gray: the hair strong…

Tasmanian Wolf
"It is the size of a small wolf, with short, smooth, hair of dusky yellowish-brown color, barred on…

French Wolves
"The common wolf is of the size of a large dog; its usual color is a yelowish gray: the hair strong…