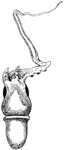Clipart tagged: ‘Cephalopod’
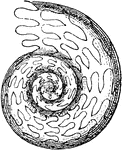
Ammonoid
"Goniatites henslowi. GONIOTITES. A genus of fossil ammonites, giving name to the family Goniatitidae,…
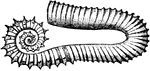
Ancyloceras
"A genus of fossil terebranchiate cephalopods, of the family Ammonitidæ, or made the type of a…

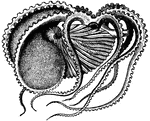
Greater Argonaut
The greater argonaut (Argonauta argo) is a cephalopod and a species of pelagic octopus also known as…
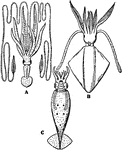
Cephalopod
The cephalopods are the mollusk class Cephalopoda characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent…
Cephalopod
A simple straight-shelled cephalopod. Where the shell has been removed, the straight sutures are shown.
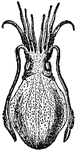
Cephalopoda
"Cephalopoda is a class of mollusks, the highest in organization of the division of the animal kingdom.…
Cuttlefish
Cephalopods are the most highly organized Molluscs. The head is distinct, carrying two large globular…
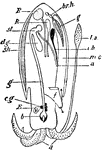
Cuttlefish Circulatory and Excretory Systems
"Diagram of circulatory and excretory systems in a Decapod-like Sepia. 1, Gill; 2, renal sac; 3, afferent…
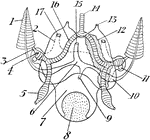
Cuttlefish Structure
"Diagram of the structure of Sepia. a., Eight short arms around mouth; l.a., one of the two long arms;…
Common Cuttlefish
The Common Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) is a mollusc in the Sepiidae family of cephalopods.
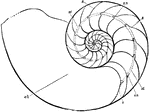
Chambered Nautilus
"Section of the shell of Nautilus pompilius, showing the septa (s, s), the septal necks (s. n., s. n.),…
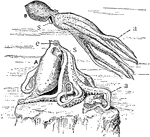
Octopus
"The Devil-fish (Octopus). A, at rest; B, swimming. a, arms, with suckers on the inner aspect; e, eye;…
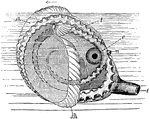
Paper Nautilus
"The Paper Nautilus (Argonauta argo). e, eye; m, mouth; f, siphon; sh, shell; t, tentacles." -Galloway,…
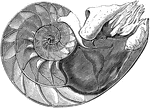
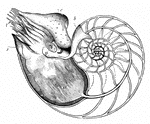
Pearly Nautilus
The Pearly Nautilus (Nautilus Pompilius) is the only living representative of a unique form of cephalopod,…

Scaphites equalis, Extinct Cephalopod Fossil
Scaphites equalis is a species of extinct cephalopods that thrived during the Cretaceous period. "A…
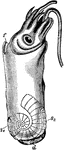
Spirula Peronii
"Spirula peronii, lateral view. d, terminal sucker; f, funnel; s1, s2, projecting portions of the shell,…
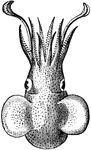
Atlantic Bobtail
The Atlantic Bobtail (Sepiola atlantica) is a cephalopod in the Sepiolidae family of bobtail squids.