Clipart tagged: ‘dredge’

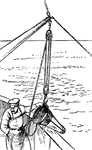
Ball's Naturalists' Dredge
"The dredges on this pattern, used in Britain for ten years after their first introduction, about the…
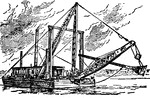
Dredge
Dredging, the excavating or scooping out of soil, mud, sand or rock under water by a machine called…
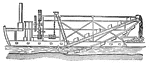
Dredge Machine
"A machine used for clearing out or deepening the channels of rivers or harbors. Dredging-machines are…
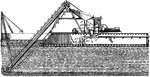
Excavating Purpose Dredger
Dredging is an excavation activity or operation usually carried out at least partly underwater, in shallow…
Hopper Dredger
"Longitudinal section of hopper dredger, employed on the River Clyde. The vessel steams to place of…

Fredrick Muller's Dredge
"Muller gives a quaint description not very unlike that used by Hall and Forbes, only the mouth of the…

Set of Sieves
"Close to the place where the dredge is emptied there ought to be a tub about 2 feet in diameter and…