Clipart tagged: ‘facial’
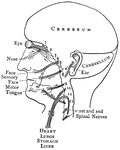
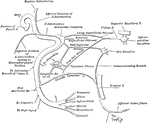
Distribution of the Cranial Nerves
"The cranial nerves are thus arranged in pairs: 1, olfactory nerves, special nerves of smell; 2, optic…
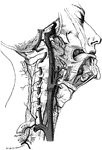
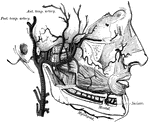
Facial Arteries
The arteries of the face and scalp. The muscle tissue of the lips must be supposed to have been cut…
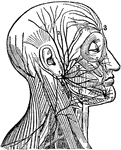
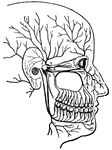
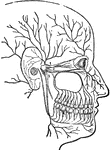
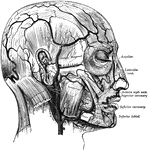
Facial Nerve
"(1) The facial nerve at its emergence from stylo-mastoid foramen; (2) temporal branches communicating…
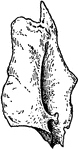
Human Lachrymal Facial Bone
Lachrymal Bone. The lachrymal are the smallest and most fragile bones fo the face. They are situated…
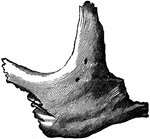
Human Malar (Cheek) Bone
Malar (cheek) bone. The malar bones form the prominence of the cheek, and part of the outer wall and…
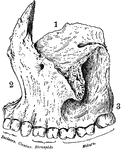
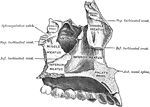
Human Maxillary (Upper Jaw) Bone
Superior maxillary bone. With it's fellow on the opposite side, it forms the whole of the upper jaw.…
Human Maxillary (Upper Jaw) Bone
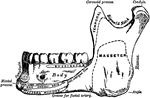
Inferior Maxillary Bone (lower jaw). It is the largest and strongest bone in the face and serves for…

Human Nostril Bone
Inferior turbinated bone, convex surface. The inferior turbinated bones are situated on the outer wall…
Human Palate Bone
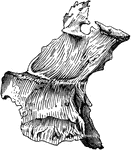
Palate bone. Palate bones form the back part of the roof of the mouth; part of the floor and outer wall…

Human Vomer Nasal Bone
Vomer bone, a single bone placed at the back part of the nasal cavity, and forms part of the septum…