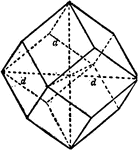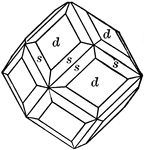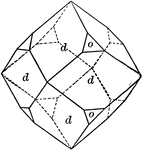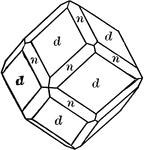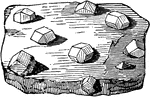
Datolite
"Monoclinic. Habit varied. Crystals usually nearly equidimensional in the three axial directions and…

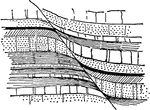
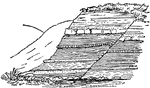
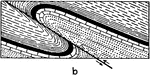
Shale Deformation
"Deformation of shale by porphyry, Burlington Railroad, east of Whitetail Gulch." -Walcott, 1901

Desert of Sahara
The Sahara is the world's largest hot desert, 9,000,000 square kilometers, almost as large as the United…
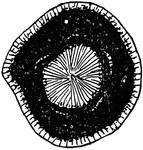
Diabantite
"Diabantite, ore material, and agate in vesicle of main basalt. The radial mass occupying the center…
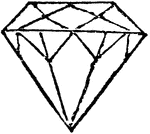
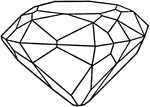
Diamond
"Pure crystalline carbon, the hardest substance known, possessing great lustre owing to its great refracting…
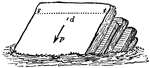
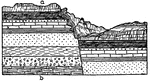
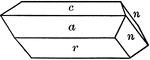
Dip
"Dip, in geology, the name given to the angle of slope of inclined rock strata, as dip in the diagram...The…
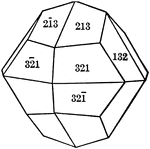
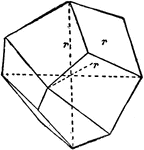
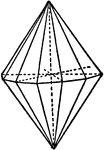
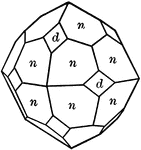
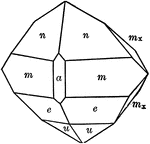
Diploid
"The diploid is a rare form found only in this class. It is composed of twenty-four faces which correspond…
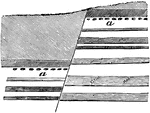
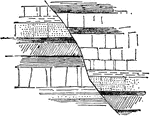
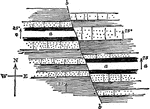
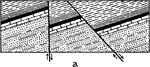
Displacement of Strata
"Section showing displacement of strata by a fault. a and a were once a continuous mass of rock." -Whitney,…
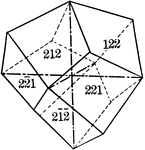
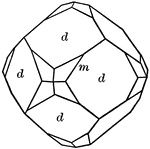
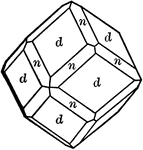
Deltoid dodecahedron
"The faces of the deltoid dodecahedron correspond to one-half those of the trisoctahedron." —…
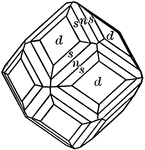
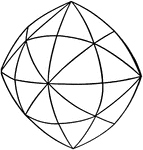
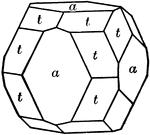
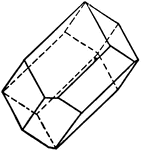
Dodecahedron, trapezohedron and hexoctahedron
"A combination of of dodecahedron, trapezohedron, and hexoctahedron." — Ford, 1912
Dolomite
"Hexagonal-rhombohedral. Crystals are usually the unit rhombohedron (cleavage rhombohedron). Faces often…
Eolianite
Eolianite or aeolianite is any rock formed by the lithification of sediment deposited by aeolian processes;…
Eozoic Strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum (plural: strata) is a layer of rock or soil with internally…
Epidote
"Monoclinic. Crystals are often much elongated parallel to the ortho-axis with a prominent development…
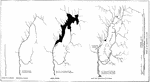
Erosion Stages
"Maps to illustrate the supposed stages in the erosion history of the Pomperaug River." -Walcott, 1901

Mendocino Coast Erosion
Erosion is the removal of solids (sediment, soil, rock and other particles) in the natural environment.…

The Falls of Niagara
The grandest falls in the world are those of the Niagara, 160 feet high. Though greatly inferior to…

Fault Scarp Slope
"View of the southeastern slope of the eastern twin of Orenaug Hill. Fault scarps bound the hummocky…

Fault Scarps
"Fault scarps of Orenaug Hill (floating block topography). The view is taken from the top of a cliff…
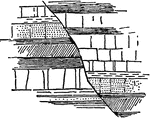
Strike Fault
"The two faults of larger throw, by which a single sheet of trap is represented in three ridges, are…

Fiords on Norway Coast
Fiords are valleys that were deeply eroded by slowly moving masses of ice called glaciers, subsequently…
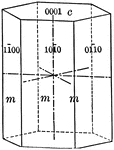
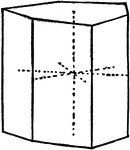
Prism of the first order
"This is a form consisting of six rectangular vertical faces each of which intersects two of the horizontal…
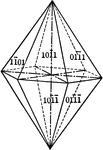
Pyramid of the first order
"This form consists of twelve isoceles triangular faces, each of which intersects two of the horizontal…

Foraminifera
These animalcule are so small that 1,000,000 are equal in bulk to only one cubic inch. They appear to…

Fossil Encrinite
When the remains of an animal or plant are exposed to the air or buried in dry earth, they generally…

Fossil Wood
"Microscopical section of Fossil Wood, from clay iron-stone nodules; Oldham." -Taylor, 1904
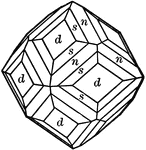
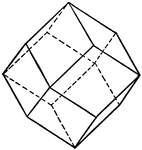
Garnet
"Isometric. Common forms dodecahedron amd trapezohedron, often in combination. Hexoctahedron observed…