Clipart tagged: ‘Girard’
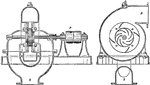
Centrifugal Pump
"A centrifugal pump differing from an ordinary centrifugal pumps in one feature only. The water rises…
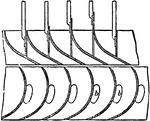
Guideblade Chamber
"The sectional form of the guideblade chamber and the wheel and the curves of the wheel vanes and guideblades,…
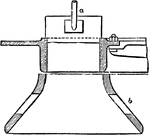
Guideblade Chamber
"The sectional form of the guideblade chamber and the wheel and the curves of the wheel vanes and guideblades,…
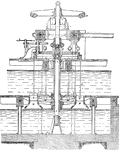
Girard Turbine
"The general sectionl elevation of a Girard turbine, in which the flow is axial. The water, admitted…