Clipart tagged: ‘grecian’

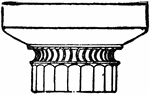
Grecian Doric Capital
"The Doric Order is, in architecture, the second of the five orders, being that between the Tuscan and…
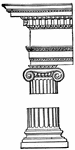
Grecian Doric Capital
"The Doric Order is, in architecture, the second of the five orders, being that between the Tuscan and…
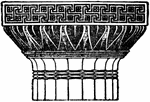
Grecian Doric Capital
"The Doric Order is, in architecture, the second of the five orders, being that between the Tuscan and…
Drontheim Frieze
"A Frieze, in architecture, is that portion of the entablature which is between the architrave and the…

Roman-Doric Frieze
"A Frieze, in architecture, is that portion of the entablature which is between the architrave and the…

Roman-Doric Frieze
"A Frieze, in architecture, is that portion of the entablature which is between the architrave and the…

Jug and Goblet
This jug and goblet are designed in a Grecian shaped ruby glass. They are cut in sunken diamond shapes.
Grecian Banner
"Greek architecture is distinguished for nothing more than for the grace and beauty of its mouldings;…

Griffin
In heraldry, the griffin is a fabulous animal, with the head and forefeet of an eagle, and the body,…

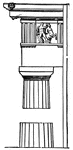
Temple of Diana at Ephesus
"The temple of Diana was the chief glory of the city. The style was Grecian. The length of the ground-plan…

Grecian Vases
"A Vase is a vessel of various forms and materials, applied to the purposes of domestic life, sacrificial…