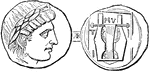
Julian
"Thus the prince, both when present and when coming, was alike victorius: and these things he achieved…

Death of Laius
"When grown up, Oedipus is told by the oracle that he would slay his father and marry his mother. On…
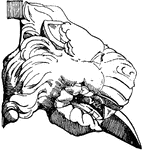
Gargoyle Lion Head
This Gargoyle Lion Head is made out of terracotta and is found in Athens, Greece.

Gate of the Lions
The Gate of the Lions is located in Mycenae, Greece. It was the entrance to the city. On top of the…

Litmus
"This instrument was long, and curved at the end. From the similarity of form the original staff received…

Lucian
"Lucian, the humorous satirist, was a native of Samosata, in Syria, and flourished towards the end of…

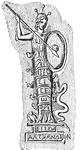
Man with ax
"Who brandishing aloft the ax of doom, That just has laid one victim at her feet, Looks round her for…

The Mound at Marathon
"Near the southern extremity of the plain of Marathon rises a conical mound, 30 feet high. it covers…
Comedy masks
"While Greek tragedt grew farther and farther away from the humor and burlesque so characteristic of…
Tragedy masks
"Tragedy masks. The origin of Greek drama is to be found in the yearly celebrations in honor of Dionysus,…

Minerva
"On Minerva's side Varro tells us that Cecrops found an olive tree and a fountain, and that on consulting…

Thesus and the Minotaur
"Thesus and the Minotaur. (From a vase-painting in the Vatican Museum.) — The Delphian Society,…

Temple of Neptune
"Paestum, the Greek Poseidonia, was a colony of Sybaris. The malarial atmosphere of the place led to…

Temple of Nike Apteros
"The first public monuments that arose after the Persian wars were erected under the auspices of Cimon,…

Greek Oblong Panel
The Greek oblong panel has a strict palmette decoration. It is found in the painted coffers (sunken…
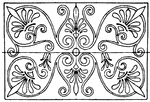
Greek Oblong Panel
The Greek oblong panel has a strict palmette decoration. It is found in the painted coffers (sunken…

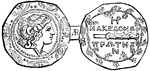
Obolus
"A small coin of ancient Greece, in later times of silver, the sixth part of an Attic drachma, equal…

Victors at the Olympic Games
"From a very remote period, the Greeks had been accustomed to engage in contests of strength and agility…

Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple of the Greek goddess Athena, built in the 5th century BC on the Athenian Acropolis.…
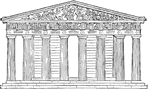
Parthenon restored
"The Parthenon stood on this highest part of the Acropolis, near its centre, and probably occupied the…

Modern Parthenon
"The Athenians, on their return to Attica, after the defeat of the Persians, found their city ruined…
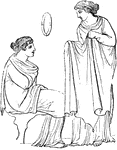
Peplus
"The peplus was a shawl which commonly formed part of the dress of females. It was often fastened…

Pericles
"So long as Pericles stood at the head of Athens in time of peace, he governed it with moderation and…

Bust of Pericles
"The enormous influence which Pericles exercised for so long a period over an ingenious but fickle people…

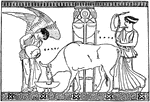
Phryxsus and ram
"When Phryxsus arrived in Colchis, he sacrificed his winger ram to Jupiter, in acknowledgement of the…

Bust of Pindar
"Pindar, though the contemporary of Simonides, was considerably his junior. He was born either at, or…

Bust of Plato
"Plato was born in Athens in 429 B.C., the year in which Pericles died. His first literary attempts…

Plutarch
"Plutarch, as the great interpreter of Greece and Rome, exerted on generations succeeding him in influence…
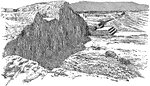
Pnyx
"Shows the bema, or platform, from which orators addressed the assembled citizens."—Webster, 1913

Polyphemus
"Theocritus asserts that there is no rememdy for Love but the Muses. He then gives an account of the…
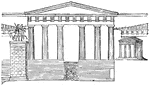
Propylea restored
"A. Pinacotheca, B. Temple of Nike Apteros, C. Pedestal of Agrippa, D. Road leading to the central entrace,…