Clipart tagged: ‘hermit crabs’
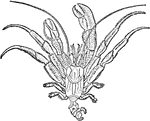
Hermit Crab
Hermit crabs are decapod crustaceans of the superfamily Paguroidea. They are not closely related to…

Hermit Crabs
An illustration of hermit craps shedding their shells and finding new ones. As hermit crabs grow they…