Clipart tagged: ‘Hypotenuse’
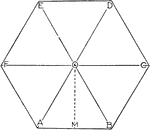
Area of Hexagon
Illustration showing how to find the area of a hexagon using the triangles that make it up.
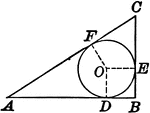
Circle Inscribed in a Right Triangle
Illustration showing the diameter of a circle inscribed in a right triangle is equal to the difference…
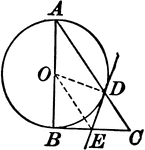
Circle With a Right Triangle
Illustration where one leg of a right triangle is the diameter of a circle. The tangent at the point…
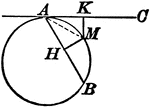
Circle With a Tangent Line and Chord
Illustration showing that from any point in the circumference of a circle, a chord and a tangent are…
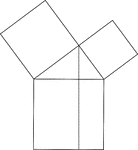
Euclid's Pythagorean Theorem Proof
Illustration used to prove the Pythagorean Theorem, according to Euclid. A perpendicular is drawn from…
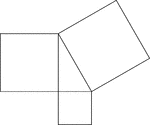
Geometric Pythagorean Theorem Proof
Illustration that can be used to prove the Pythagorean Theorem, the sum of the squares of the legs is…
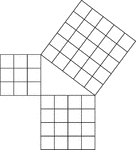
Geometric Pythagorean Theorem Proof
Illustration that can be used to prove the Pythagorean Theorem, the sum of the squares of the legs is…
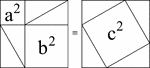
Pythagorean Theorem Proof by Rearrangement
A visual illustration used to prove the Pythagorean Theorem by rearrangement. When the 4 identical triangles…
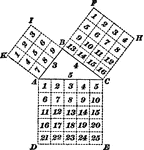
Right Triangle
"In any right triangle, the square described on the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares described…
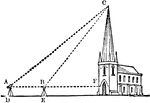
Triangle with Church
An illustration of a triangle comprised of a church and two lines. This illustration can be used to…
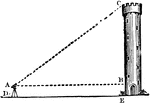
Triangle with Tower
An illustration of a triangle comprised of a tower and two lines. This illustration can be used to determine…
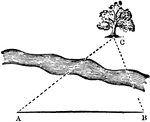
Triangle with Tree
An illustration of a triangle comprised of a tree and two lines. This is an example of a problem that…
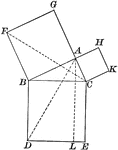
Right Triangle
Illustration of a right triangle used to show the Pythagorean Theorem (the square of the hypotenuse…
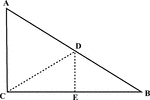
Right Triangle With Midpoint of Hypotenuse Drawn
Illustration of a right triangle with the midpoint of the hypotenuse drawn.