Clipart tagged: ‘leech’
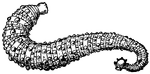
Leech
Leeches are characterized by the fact that they have no lateral appendages, but are furnished with a…
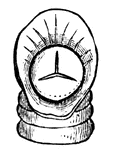
Leech
Leeches are characterized by the fact that they have no lateral appendages, but are furnished with a…

Leech
A class of suctorial worms found in bodies of water, marshes, and other moist places. There are many…

Medicinal Leech
The medicinal leech is a leech used in bloodletting. It lives in fresh water, and is common in Germany,…