Wheel Barometer
"The whole length of the tube of the wheel barometer, from C to A, is 34 or 35 inches, and it is filled…
Wheel Barometer
"As the mercury rises and lowers in the barometer, the float F turns the index, I. Index I points to…

Wheel Barometer
The wheel barometer consists of a siphon barometer, the two branches of which have usually the same…

Wheel Rotation
"Rotation of a Wheel. The same force which throws the wire away from the mercury, will cause the rotation…
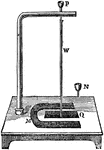
Wire Vibration
"Vibration of a wire. A conducting copper wire, w, is suspended by a loop from a hook of the same metal,…

