Clipart tagged: ‘myopia’
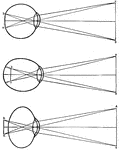
Human Eye
Diagrams of how an image is displayed with a normal eye (top image), myopic or nearsighted eye (middle…
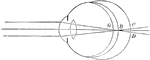
The Position of the Retina in Near and Far Sight
A flattened shape of the globe of the eye causes farsightedness and an elongated shape of the globe…