Clipart tagged: ‘"nerve trunk"’
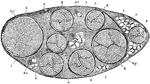
Nerve Trunk
Each nerve trunk is composed of a variable number of different sized bundle (funiculi) of nerve fibers…
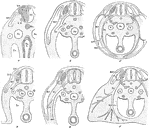
Development of the Spinal Nerve
Development of the spinal nerves. A, Formation of nerve roots. B, Formation of nerve trunk (N).C, Formation…