Clipart tagged: ‘peridia’
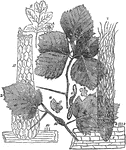
Cellular structure of peridia
"Under the power of about 90 diameters the general character of the peridia is seen. They are densely…

Potato Diseases at a Microscopic Level
"It is not unusual to fine a decayed spot in the center of potatoes otherwise apparently in good condition.…