Clipart tagged: ‘pith’
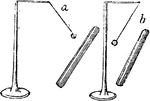
Electrical Attraction
"If an excited substance be brought near a ball made of pith, or cork, suspended by a silk thread, the…
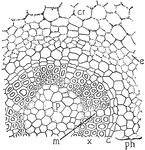
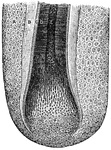
Botrychium
This illustration shows the cross-section of a stem of Botrychium: p, pith; x, xylem; m, ray; c, cambium;…
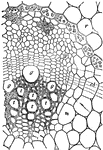
Cambium
"Transverse section of an open fibro-vascular bundle. c, cambium; cb, continuation of cambium between…
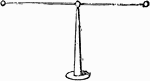
Electroscope
"One of the simplest instruments of this kind consists of a metallic needle, terminated at each end…
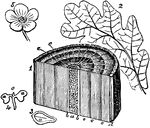
Section of Branch Showing Exogen
"Exogen. 1. Section of a branch of three years' growth: a, medulla or pith; b b, medullary sheath; e…
!["Longitudinal tangential section of [maple], showing the ends of the medullary rays." - Century, 1889](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/73300/73379/73379_maple_mth.gif)
Longitudinal Tangential Section of Maple
"Longitudinal tangential section of [maple], showing the ends of the medullary rays." - Century, 1889
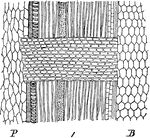
Medullary Rays of Maple
"Longitudinal radial section through the wood of a branch of maple one year old: P, pith; B, bark."…
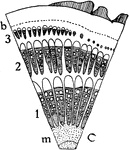
G. Scandens Unusual Stem Growth
"Diagram showing some types of unusual growth in thickness...C, portion of a cross section of stem of…
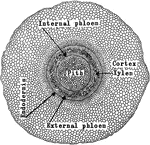
A. Pedaium Stem
"Adianium pedatum: transverse section of stem, showing the amphiphloic siphonostele." -Stevens, 1916
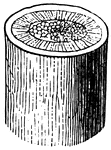
Woody Stem
The central part of the stem is the pith, then is the cellular tissue and finally the bark.
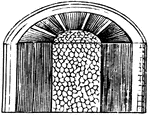
Woody Stem
The central part of the stem is the pith, then is the cellular tissue and finally the bark.