Clipart tagged: ‘Propagated’
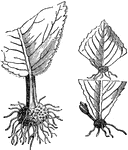
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…
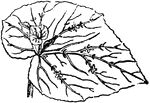
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…
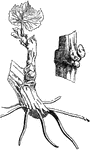
Single Eye
"This mode of propagation is performed by cutting the branches into short lengths, each containing one…