Clipart tagged: ‘reflex’
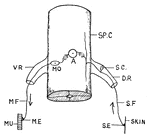
Reflex Action
Illustration of the reflex action of an animal. SE is the sensory nerve-ending. A stimulus passes through…
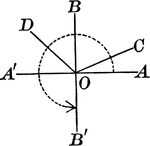
Acute, Obtuse, Straight, Right, And Reflex Angles
An illustration showing acute, obtuse, straight, right, and reflex angles.
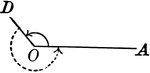
Obtuse And Reflex Angles
An illustration showing an angle the is greater than a right angle and less than a straight angle. This…
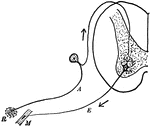
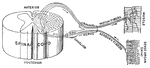
Reflex Arc
"Diagram of the simple reflex arc. R, receptor; A, afferent (sensory) neuron; E, efferent (motor) meuron;…