Clipart tagged: ‘ruminant’

Camel
"Camel is a genus of ruminant quadrupeds, characterized by the absence of horns; a fissure in the upper…
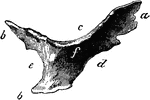
Cardiac Bone of an Ox
Right cardiac bone of an ox. Labels: a, anterior angle; b, posterior angles; c, superior border; d,…
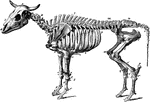
Ox Skeleton
The skeleton of an ox. Axial Skeleton. The skull. Cranial Bones- occipital, 1: b, parietal, 2; a, frontal,…
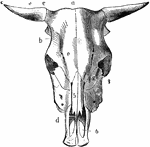
Ox Skull
Skull of an ox, superior aspect. Labels: a, frontal crest; b, lateral crest; c, horn core; d, nasal…
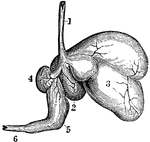
The Stomach of a Sheep
Ruminants (those animals that chew the cud), as the sheep, have a stomach with four cavities. Labels:…
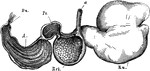
Stomach of a Sheep
Stomach of an sheep seen from the left side- the last three compartments are laid open and reflected…

Stomach of a Sheep
Compartments of a ruminant stomach, laid open. A, rumen- a, pillars; b, papilla; c, esophageal orifice.…
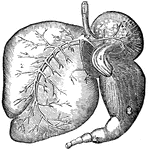
Stomach of an Ox
Ruminants (those animals that chew the cud), as the ox, have a stomach with four cavities. Labels: 1,…


