Clipart tagged: ‘sec’
Unit Circle
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. The…
Unit Circle Labeled At Quadrantal Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
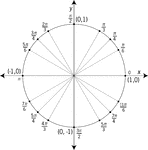
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
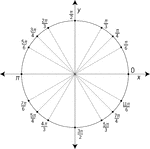
Unit Circle Labeled At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
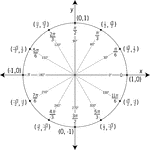
Unit Circle Labeled In 30° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
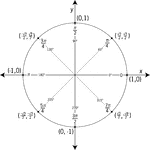
Unit Circle Labeled In 45 ° Increments
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
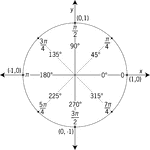
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
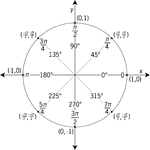
Unit Circle Labeled In 45° Increments With Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
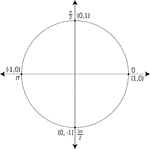
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. All…
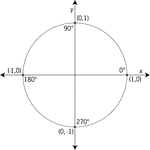
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
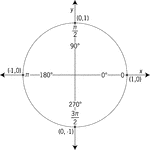
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
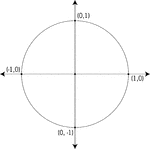
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. At each…
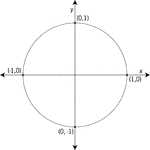
Unit Circle Labeled With Quadrantal Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
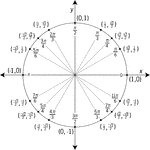
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
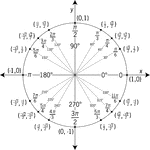
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
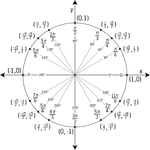
Unit Circle Labeled With Special Angles And Values
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane with…
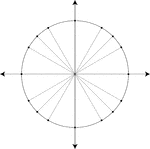
Unit Circle Marked At Special Angles
Illustration of a unit circle (circle with a radius of 1) superimposed on the coordinate plane. All…
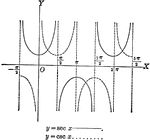
Secant and Cosecant Curves, y=sec x and y=csc x
Secant and Cosecant curves plotted from negative pi to 2 pi. Graph of y=sec x and y=csc x.