Clipart tagged: ‘syphon’
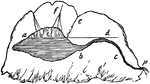
Intermitting Spring
"A mountain and spring, showing how the principle of the syphon operates to produce the effect described.…
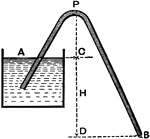
Siphon
A siphon (also spelled syphon) is a continuous tube that allows liquid to drain from a reservoir through…
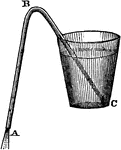
Syphon
"Take a tube bent like the letter U, and, having filled it with water, place a finger on each end, and…
