Search for "actors"
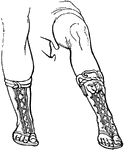
Cothurnus
"A boot. Its essential distinction was its height; it rose above the middle of the leg, so as to surround…

Persona
"A mask. Masks were worn by Greek and Roman actors in nearly all dramatic representations. This custom…

Persona
"A mask. Masks were worn by Greek and Roman actors in nearly all dramatic representations. This custom…
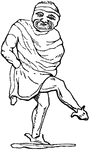
Soccus
"Soccus was nearly if not altogether equivalent in meaning to Crepida, and denoted a slipper or low…

Comte de Barras
A French Jacobin, born in Province, in 1755, of an ancient family; served as second lieutenant in the…

William J. Florence
William Jermyn Conlin (July 26, 1831, Albany, N.Y. – Nov. 19, 1891, PA), better known by his stage…
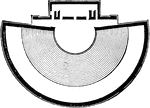
Ground Plan of the Theatre at Iassus
The theatres were originally built on a very large scale to accommodate the large number of people on…

Theatrical Costume
One of the more prominent places people see costumes is in theater, film and on television. In combination…
