This human anatomy ClipArt gallery offers 69 illustrations of human embryonic and fetal development, including external and dissected views of general development and development of specific systems progressing from fertilization to birth. Also includes views of the uterus and placenta as the embryo or fetus develops.
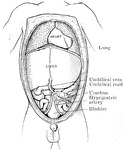
Abdomen of Fetus
The abdominal and thoracic viscera of a five months fetus. The large liver and large size if its left…
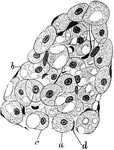
Developing Adipose Tissue in Fetus
A lobule of developing adipose tissue from an eight month fetus. Labels: a, Spherical or, from pressure,…
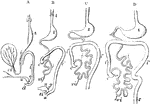
Development of the Alimentary Canal
Outlines of the form and position of the alimentary canal in successive stages of its development. A,…
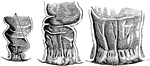
Development of the Anal Cavity
The anal cavity and lower part of the rectum in the fetus. Left figure is four month. Middle figure…
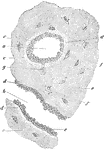
Formation of Compact Bone in a Human
Transverse section of femur of a human embryo about eleven weeks old. Labels: a, rudimentary Haversian…
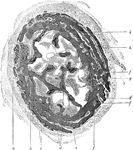
Developing Bone
Cross section of developing bone of human fetus of four months. Labels: a, periostem; b, boundary between…
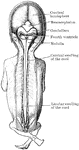
Brain and Spinal Cord of Fetus
Human fetus in the third month of development, with the brain and spinal cord exposed from behind.
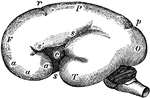
Fetal Brain at Six Months
Side view of fetal brain at six months, showing commencement of formation of the principal fissures…
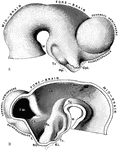
Brain of Embryo
The brain of a human embryo in the fifth week. A, Brain as seen in profile. B, Mesial section through…
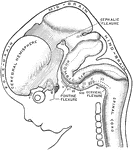
Brain of Embryo
Profile view of brain of a human embryo of ten weeks. The various cranial nerves are indicated by numerals.…
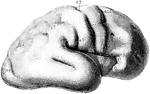
Brain of Fetus
The left cerebral hemisphere, from a fetus in the early part of the seventh month of development. Labels:…
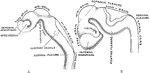
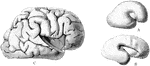
Development of Human Brain
Two stages in the development of the human brain. A. Brain of an human embryo of the third week. B.…
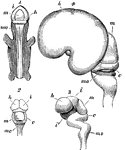
Development of the Brain
Early stages in development of human brain. 1, 2, 3, are from an embryo about seven weeks old; 4, about…
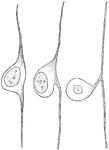
Development of Cell from Spinal Ganglion
Three stages in the development of a cell from a spinal ganglion.
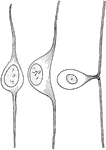
Development of a Cell from the Spinal Ganglion
Three stages in the development of a cell from a spinal ganglion.

Chorion Villi
Very soon after the entrance of the ovum into the uterus, in the human subject, the outer surface of…
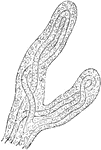
Magnified View of Chorion Villi
Very soon after the entrance of the ovum into the uterus, in the human subject, the outer surface of…
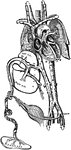
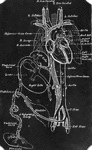
Diagram of Fetal Circulation
Plan of fetal circulation. In this plan, the figured arrows represent the kind of blood, as well as…

Corpus Lutea of Different Periods
Corpus lutea of different periods. B, corpus luteum of about the sixth week after impregnation, showing…
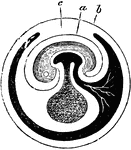
Fecundated Egg
Fecundated egg with allantois nearly complete. Labels: a, inner layer of amniotic fold; b, outer layer;…

Impregnated Egg
Impregnated egg, with commencement of formation of embryo; showing the area germinativa or embryonic…
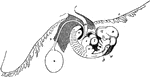
Embryo at Fourth Week
A human embryo of the fourth week. I, the chorion; 3, part of the amnion; 4, umbilical vesicle with…
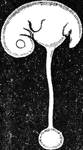
Embryo of Fifth Week
Human embryo of fifth week with umbilical vesicle. The human umbilical vesicle never exceeds the size…

Embryo Showing Course of Circulation
Diagram of young embryo and its vessels, showing course of circulation in the umbilical vesicle; and…
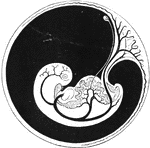
Embryo Showing Course of Circulation
Diagram of embryo and its vessels, showing course of circulation. The large umbilical arteries are seen…
Head of an Embryo
A, Magnified view of the head and neck of a human embryo of three weeks. Labels: 1, anterior cerebral…
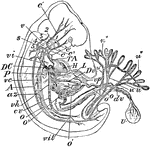
Human Embryo
"Early Human Embryo, giving diagrammatically the principal vessels antecedent to the establishment of…
Longitudinal Section of an Embryo
Diagram of a longitudinal section of an embryo, showing the different areas of the blastodermic vesicle.…
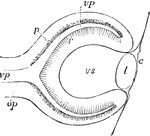
Eye of Fetus of Four Weeks
Diagrammatic sketch of a vertical longitudinal section through the eyeball of a human fetus of four…
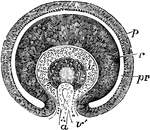
Eye of Fetus of Four Weeks
Transverse vertical section of the eyeball of a human embryo of four weeks. The anterior half of the…
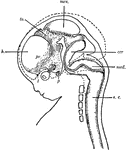
Human Fetus
"Diagram of head and brain of human foetus six weeks old (heavy boundaries). The dotted line indicates…
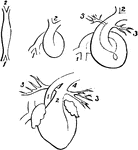
Fetal Heart in Successive Stages of Development
Fetal heart in successive stages of development. 1, venous extremity; 2, arterial extremity; 3, pulmonary…
Human Spermatozoa
"One of the numberless microscopic bodies contained in semen, to which the seminal fluid owes its vitality,…
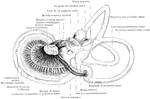
Labyrinth of Fetus
Membranous labyrinth of a five months' fetus, viewed from its postero-mesial aspect.
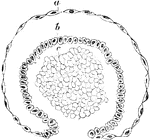
Development of Malpighian Capsule
Transverse section of a developing Malpighian capsule and tuft from a fetus at about the fourth month.…
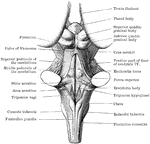
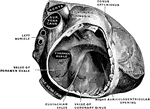
Back View of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Back view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
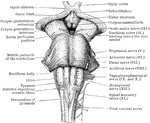
Front view of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Front view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
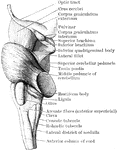
Lateral View of Medulla, Pons, and Mesencephalon
Lateral view of the medulla, pons, and mesencephalon of a full term human fetus.
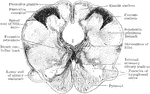
Transverse Section Through Closed Part of Fetal Medulla
Transverse section through the closed part of the fetal medulla immediately above the decussation of…

Transverse Section Through the the Medulla
Transverse section through the lower end of the medulla of a full term fetus.
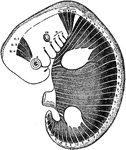
Myotomes in an Embryo
Scheme to illustrate the disposition of the myotomes in the embryo in relation to the head, trunk, and…
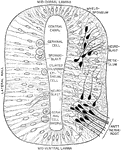
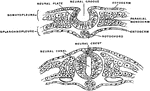
Section Through Early Neural Tube
Transverse section through the early neural tube, diagrammatically represented. The left side of the…
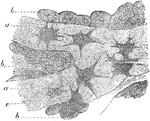
Osteoblasts
Osteoblasts from the parietal bone of a human embryo, thirteen weeks old. Labels: a, bony septa with…
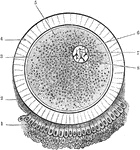
Ovum
The ovum and its coverings. The corona radiata, which completely surrounds the ovum, is only represented…
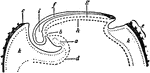
Developing Ovum
Diagram of a developing ovum, seen in longitudinal section. Labels: a, pericardium; b, bucco-pharyngeal;…

Maturation of the Ovum
The maturation of the ovum. A, An ovum at the commencement process. B, After the formation of the spindle.…
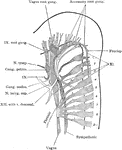
Peripheral Nerves of Human Embryo
Reconstruction of peripheral nerves of human embryo of five weeks.
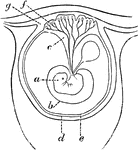
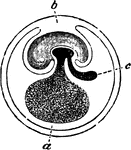
Early Formation of the Placenta
Diagram of an early stage of the formation of the human placenta. Labels: a, embryo; b, amnion; c, placental…
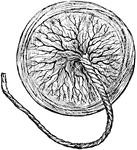
Human Placenta
The organ of attachment of a vertebrate embryo or fetus to the wall of the uterus or womb of the female.

Section of Placenta
Section of human placenta at end of pregnancy. The fetal blood vessels have been injected; the maternal…
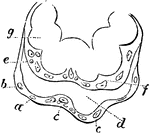
Placental Villus
Extremities of a placental villus. Labels: a, lining membrane of the vascular system of the mother;…

Pyramidal Cells of the Brain
The developmental stages exhibited by a pyramidal cell of the brain. Labels: a, neuroblast with rudimentary…

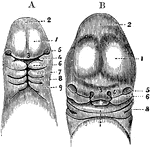
Rectum and Anal Canal in Fetus
The anal canal and rectum in a fetus. A, aged 4 to 5 months; B, 6 moths; C, 9 months. In each he anal…