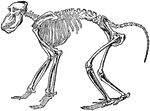
Chacma Baboon Skeleton
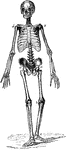
"The skeleton, more especially in the higher forms, is in the main similar to that of man, so that only…
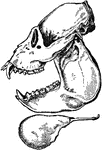
Side View of Howler Monkey
A side view of the howler monkey skull. The monkey have four sharp canines, long teeth on skull, on…
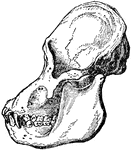
Adult Male Orangutan Skull Viewed from Side
An illustration of an adult male orangutan viewed from the side. The orbit part of the skull is more…
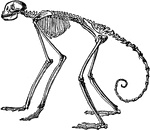
Side View of Skeleton of South American Spider Monkey
"In the other forms the number (vertebrae) varies between twenty and thirty three, the latter being…
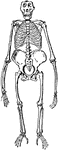
Front View of Gorilla Skeleton
"The greatest absolute length of the fore—limb occurs in the gorilla and the orangutan. The humerus…
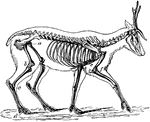
Skeleton of the Deer
"The bones in the extremities of this the fleetest of quadrupeds are inclined very obliquely towards…
Wing of Bird
"Shows how the bones of the arm (a), forearm (b), and hand (c), are twisted, and form a conical screw."—Pettigrew,…
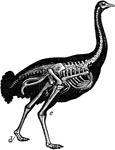
Skeleton of Ostrich
"Shows the powerful legs, small feet, and rudimentary wings of the bird; the obliquity at which the…
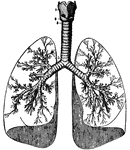
Human Lungs
Human lungs. 1 and 2 make up the larynx, or voice box. 1 is thyroid cartilage, 2 is cricoid cartilage.…
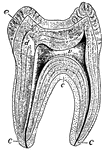
Human Tooth
A sectional view of a human molar. The roots, or fangs, are shown covered by a layer of bone called…
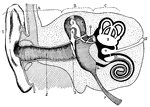
Human Ear
A diagram of the human ear. It is divided into the outer ear - A, middle ear - B, and inner ear - C.…
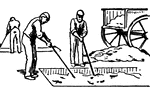
First Stage in Glue Manufacturing
This illustration shows the first stage in the manufacturing of glue. The material used for making the…
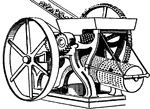
Cross Mill and Sieves (Glue)
This illustration shows a cross mill and the sieves used to crush and filter bones in glue manufacturing.
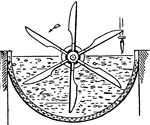
Wash Box for Removing Lime
This illustration shows a wash box used for removing lime from materials used in glue manufacturing.
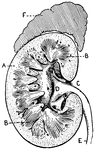
Section of Human Kidney
This illustration shows a section of a human kidney (A, Cortical substance; B, Pyramids; C, Hilum; D,…
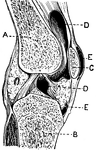
Section of the Knee
This illustration shows a section on the knee (A, Femur; B, Tibia; C, Patella; D, Synovial sac; E, bursæ).…
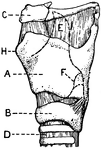
Lateral Aspect of Larynx
This illustration shows a lateral aspect of the larynx and its multiple parts (A. Thyroid Cartilage;…
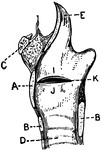
Vertical Section of Larynx
This illustration shows a vertical section of the larynx and its many parts (A. Thyroid Cartilage; B.…
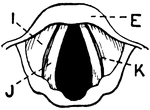
Vocal Cords Seen from above During Quiet Breathing
This illustration shows the vocal cords, seen from above during quiet breathing (A. Thyroid Cartilage;…
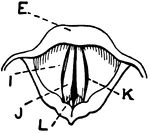
Vocal Cords Seen from above During Phonation
This illustration shows the vocal cords as seen from above during phonation (A. Thyroid Cartilage; B.…
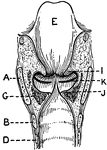
Longitudinal Section of Larynx Seen from Behind
This illustration shows a longitudinal section of the larynx as seen from behind (A. Thyroid Cartilage;…
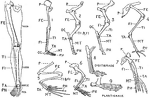
Human Leg (Front View), and Comparative Diagrams showing Modifications of the Leg
This illustration shows a human leg (front view), and comparative diagrams showing modifications of…
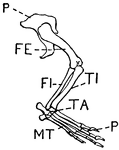
Leg of Crocodile
This illustration shows the leg of a crocodile. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
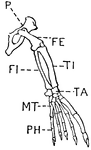
Leg of Seal
This illustration shows the leg of a seal. P. Pelvis, FE. Femur, TI. Tibia, FI. Fibula, TA. Tarsus,…
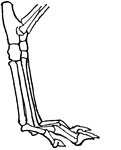
Leg of Dog
This illustration shows the leg of a dog. This leg is digitigrade. Animals with digitigrade legs walk…
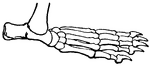
Leg of Bear
This illustration shows the plantigrade leg of a bear. Plantigrade means that the animal walks flat…
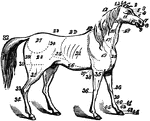
Horse
The anatomy of a horse. 1, ears; 2, forelock; 3, forehead; 4, eyes; 5, eye-pits; 6, nose; 7, nostril;…
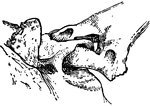
Shackle Joint from the Exoskeleton of a Siluroid Fish
"A joint involving the principle of the shackle. Specifically, in anatomy, a kind of articulation found…

Armadillo - Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton or Dermoskeleton
An illustration of a pichiciago, a small burrowing armadillo. The front half of the animal is covered…