Clipart tagged: ‘Approximate Ellipse with Four Centers’
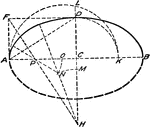
Approximate Ellipse with Five Centered Arc
"This (five centered arc) method is based on the principle that the radius of curvature at the end of…
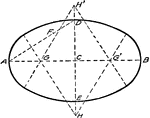
Approximate Ellipse with Four Centers
"Join A and D. Lay off DF equal to AC-DC. Bisect AF by a perpendicular crossing AC at G and intersecting…