Clipart tagged: ‘begonias’
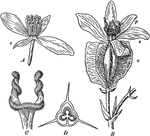
Begonia
"Begonia Flowers. A, staminate flower; B, pistillate flower; C, twisted stigmas, enlarged; D, cross-section…
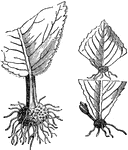
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…
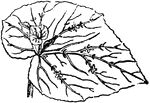
Leaf Cuttings
"Many plans may be propagated by planting their leaves or portions of their leaves as cuttings, as,…