Clipart tagged: ‘breathing’
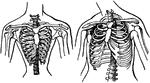
Abnormal Chest
On the right is a normal sized chest and on the left is chest as it is in one that has been girt round…
![Torso of the Statue known as Venus of Melos (left) and New York Fashion, 1898 (right). "Since abdomen and chest alternately expand and contract in healthy breathing, anything which impedes their free movement is to be avoided. The tight lacing which is still indulged [in 1900] by those who think a distorted form beautiful, seriously impedes one of the most important functions of the body, and leads not only to shortness of breath and an incapacity for muscular exertion, but in many cases to actual deformity or disease." — Newell, 1900.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/36200/36290/corset_36290_mth.gif)
Effect of Corset Use on Respiration
Torso of the Statue known as Venus of Melos (left) and New York Fashion, 1898 (right). "Since abdomen…
![Torso of the Statue known as Venus of Melos (left) and New York Fashion, 1898 (right). "Since abdomen and chest alternately expand and contract in healthy breathing, anything which impedes their free movement is to be avoided. The tight lacing which is still indulged [in 1900] by those who think a distorted form beautiful, seriously impedes one of the most important functions of the body, and leads not only to shortness of breath and an incapacity for muscular exertion, but in many cases to actual deformity or disease." — Newell, 1900.](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/36200/36291/corset_36291_mth.gif)
Effect of Corset Use on Respiration
Torso of the Statue known as Venus of Melos (left) and New York Fashion, 1898 (right). "Since abdomen…
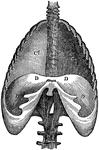
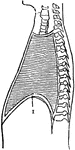
The Diaphragm
The diaphragm, which is the principal muscle that act sin breathing. Here you have the cavity of the…
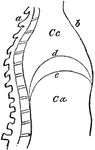
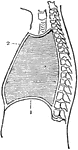
The Diaphragm
Diaphragm of the diaphragm and it's placement in the chest. Let a represent the spinal column,…

Gills (Branchial Arch of Perch)
This illustration shows the gills (breathing apparatus) of a perch, as well as the specific veins and…

Gills (Crayfish)
This illustration shows the thorax of a crayfish with a portion of the carapace removed to show the…
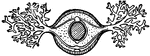
Gills (worm)
This illustration shows a transverse section of a worm with external gills. Gills are the breathing…
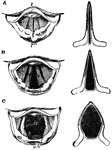
The Larynx in Different Conditions of the Glottis
The larynx as seen by means of the laryngoscope in different conditions of the glottis. Labels: A, while…
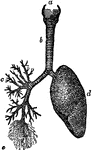
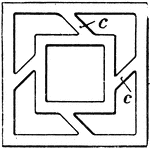
Structure of the Lungs
Diagram showing the structure of the lungs. At d is the left lung, and at c are represented…
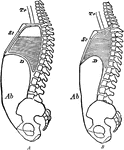
Changes during Respiration
Diagram to show the changes in the sternum, diaphragm, and abdominal wall in respiration. Labels: A,…
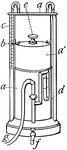
Spirometer
"A contrivance for measuring the extreme differential capacity of the human lungs. The instrument most…