Clipart tagged: ‘daniell’
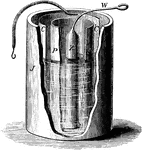
Daniell Cell
The Daniell cell (var. sp. Daniel cell), also called the gravity cell or crowfoot cell was invented…

Daniel Cell
The first two-fluid cell was incented by Daniell, and English electrician in 1836..." -Atkinson 1903
