Clipart tagged: ‘deflection’

Deflection of Wood Using Known Weights
"Place a known weight (say 100 g.) in the scale-pan, and to this weight add the weight of the clevis…
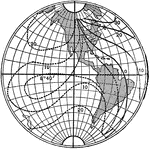
Isogonic Lines of Earth
"The magnetic poles of the earth do notc oincide with its geographical poles and, condequently, in some…
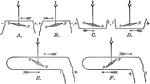
Deflection of te Magnetic Needle by the Electric Current
"Oersted's experiements are illustrated...which shows, at A, B, C and D, the four different positions…
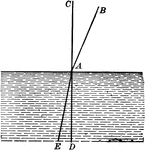
Atmospheric Optics
"BA is the ray of light passing through a rare medium (as, for instance, air); and upon its entrance…