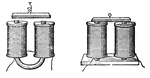Clipart tagged: ‘electric current’
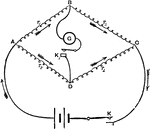
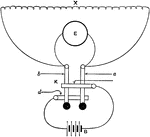
Arrangement of Battery, Resistance, and Galvanometer
"Represents in diagram the arrangement of the battery, resistance, and galvanometer. There are two keys,…
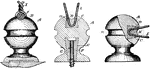
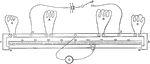
Electric Wire Insulator
An insulator is a material that resists the flow of electric current. An insulating material has atoms…

Electromagnet
"A magnet which owes its magnetic properties to the inductive action of an electric current." -Whitney,…

Astatic Galvanometer
"Astatic galvanometer, an instrument which consists of a pair of similar needles magnetized, with their…
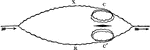
Differential Galvanometer
"The galvanometer consists of two distinct coils of wire, each having the same resistance, and having…