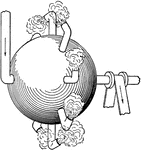
Hero's Simple Steam Turbine
A simple steam turbine by Hero of Alexandra during first century AD. The turbine consists of a hollow…
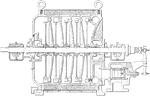
Sectional View of Kerr Turbine
"The shaft, where it passes through the diaphragm, is fitted to a bronze bushing with a few thousandths…
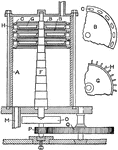
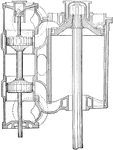
Real and Pichon Compound Steam Turbine
"A compound turbine was patented by Real and Pichon, the idea being to reduce the velocity of rotating…
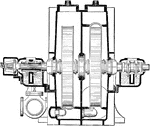
Cross Sectional View of Two Stage Condensing Terry Steam Engine Turbine
A two stage condensing Terry turbine from a steam engine. The steam, entering from the top, rotates…
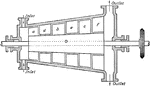
Wilson's Compound Steam Turbine
"A view of Wilson's invention is shown; a, b, and c, are vance which are attached to and rotate with…
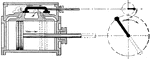
Valve with Lap of Steam Engine Where Steam Enters the Slide Valve Compartment
"The maximum displacement of the valve is attained when the eccentric is horizontal. In this position…
Slide Valve of Steam Engine
"The amount that the valve overlaps the steam ports is called the lap of the valve. It will at once…
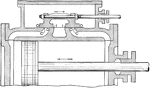
Cross Sectional View of the High Pressure Cylinder of Piston Valve from USS Massachusetts
"This valve consists of two pistons connected by a sleeve through which the valve rod passes. This valve…
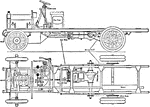
Halley's Van or Lorry with Internal Combustion Vehicle Side and Chassis View
A side internal and chassis view of the Halley's Van or Lorry. The vehicle have a 20 horsepower engine…
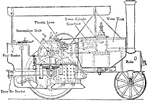
Side and Inside View of Steam Operated Vehicle
A side and inside view of the superheated steam vehicle. Water is heated by a heat transferred by the…
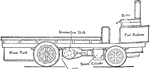
Steam Wagon with Two Side Chains Transmitting Drive
An illustration of a steam wagon with a transmission with two side chains. The boiler is located on…
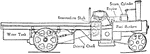
Steam Wagon with Single Chain Transmitting Drive
A steam wagon with single chain, connecting the back wheels to the differential gear. The engine is…
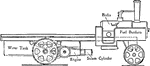
Wagon with Steam Engine and Transmission Gearing with Double Helical Gear
"The transmission on the first type of vehicle is by means of gearing throughout, and is completely…
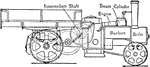
Steam Operated Wagon with Transmission Gearing with Double Helical Gear
A steam operated wagon with two speed gear. The gears are located at the intermediate shaft, moving…
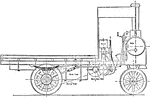
Yorkshire Steam Wagon Patent
A Yorkshire steam wagon patent with unique boiler construction. The wagon operates with the drive chain…
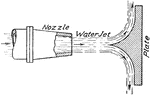
Water Jet Deflected 90 Degrees Measuring Force
"If the velocity of impact of the jet is V feet per second, its velocity in the same direction after…