Clipart tagged: ‘Fossils’

Sigillaria, An Ancient Tree
Sigillaria is the generic name assigned to this ancient arborescent lycopod. Occassionally the trunks…
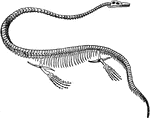
Fossil
This illustration shows the ancient fossile of an amphibian. Fossils are the mineralized or otherwise…
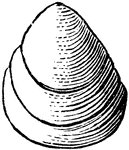
Lingula Antigua
The Lingula antigua is a little bivalve shell belonging at the bottom of the class Brachiopoda. The…
Lingula Prima
The Lingula prima is a little bivalve shell belonging at the bottom of the class Brachiopoda. The inarticulate…
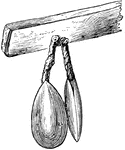
Modern Lingula
Lingula is a genus of brachiopods within the class Lingulata. Lingula is among the few brachiopods surviving…
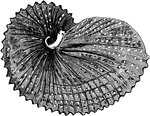
Paper Nautilus Octopuses
The argonauts (genus Argonauta, the only extant genus in the Argonautidae family) are a group of pelagic…

Paper Nautilus Octopuses
The argonauts (genus Argonauta, the only extant genus in the Argonautidae family) are a group of pelagic…
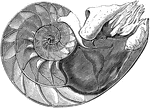
Pearly Nautilus
The Pearly Nautilus (Nautilus Pompilius) is the only living representative of a unique form of cephalopod,…
Sandstone
Along the south shore of Lake Superior is a sandstone once regarded as belonging to the Potsdam, but…

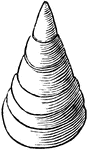
Scaphites equalis, Extinct Cephalopod Fossil
Scaphites equalis is a species of extinct cephalopods that thrived during the Cretaceous period. "A…
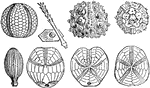
Sea Urchin Fossils
An illustration of various sea urchin fossils. "1, Palaeechinus; Carboniferous; 2, A plate and radiole…
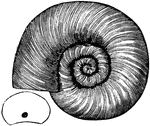
Coiled Chambered Shell
Following the species of simple septa and straight shells, came the Trocholites ammoulus, of simple…

Coiled Chambered Shell
The Clymenia Sedgwickii represents a coiled shell with angulated or bent septa.
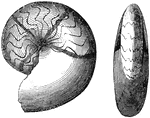
Coiled Chambered Shell
Goniatites are extinct ammonoids, shelled cephalopods related to squid, octopus, and belemnites, that…

Straight Chambered Shell
Chambered shell, endless in their variations, in the earliest periods were a species with simple septa…

Coiled Chambered Shell
Baculites is a genus of extinct marine animals in the Phylum Mollusca and Class Cephalopoda. They are…
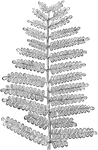
Pecopteris Tree Fern
Pecopteris, frond of an ancient tree fern, was a form genus of leaves from several unrelated plant groups…
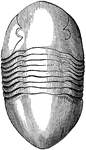
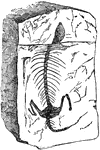
Asaphus Gigas a Trilobite
Asaphus is a genus containing at least 35 species of Ordovician trilobites found primarily in Europe.…
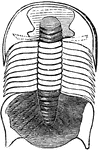
Dicellocephalus Minnesotenis a Trilobite
Trilobites ("three-lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Why the trilobites…
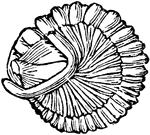
Dicellocephalus Minnesotenis a Trilobite
Trilobites ("three-lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Why the trilobites…

Dicellocephalus Minnesotenis a Trilobite
Trilobites ("three-lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita.The earliest…