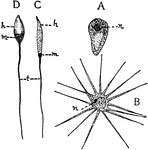
Spermatozoa
"Types of spermatozoa. A, from the round worm (Ascaris) with a cap, somewhat amaeboid; B, from the Crayfish,…
Tadpole
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…

Tadpole
"The Tadpole is the larva of the anurous amphibia, sometimes so far extended as to include larvaæ…
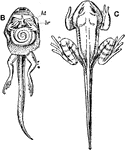
Inside and Outside View of Tadpole During Metamorphosis
The illustration is showing both inside and outside view of the tadpole. The left inside view shows…
Newly hatched tadpole
"Figure 5 shows the form of the tadpole when first hatched, which usually takes place about four weeks…

Spadefoot Toad
Scaphiopus holbrooki. Illustration of the American spadefoot toad, native to Canada, the United States,…

Surinam Toad
Its color is brownish olive, above and whitish below. It is sometimes 7 inches long, and has a peculiarly…

Surinam Toad
"When the female has laid her eggs, the male takes them and piles them on her back." Her skin becomes…