Clipart tagged: ‘leaf epidermis’
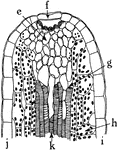
P. Sinensus Hydatode
"Radial longitudinal section through a hydatode from the leaf margin of Primula sinensis. i, upper,…
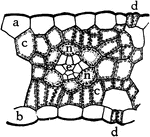
Indian Corn Leaf Cells
"Cross section of a portion of a leaf of Indian corn. a, upper and b, lower epidermis; c, c, palisade…
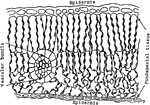
Leaf Epidermis
"Cross section of a portion of the blade of a leaf, showing upper epidermis at a, lower epidermis at…
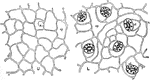
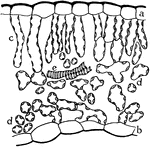
Leaf Epidermis
"Lizard's tail (Saururus cernuus). Portions of leaf-epidermis; U, upper epidermis; L, lower epidermis;…
Longleaf Pine (Pinus palustris Mill.). Two-thirds natural size. epidermis of leaf (magnified)
The longleaf pine commonly found in the South Atlantic and Gulf States. The leaves are 9 to 12 inches…
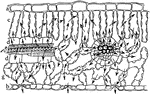
Leaf Water Flow
"Semi-diagrammatic cross section of a leaf showing by arrows how the water passes from the tracheal…