Clipart tagged: ‘membrane’

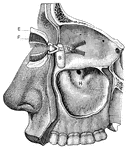
Red-Throated Dragon
"The Red-Throated Dragon shows a large membranous expansion (b b) situated between the anterior (d d)…
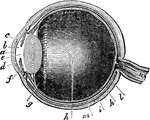
Eye
"Next in order is the aqueous humor, b, e, in the middle of which is the iris, d, c. Behind the pupil…
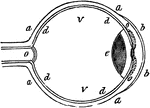
Eye
"a, sclerotic membrane; b, cornea; d, retina; o, optic nerve; v, vitreous humor." -Comstock 1850

Micrococci
"Characteristic groups of Micrococci. Zoogloea stage of a Micrococcus, forming a close membrane on infusion."…
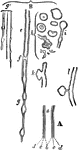
Nerves
"a, axis cylinder; b, inner border of white substance; c, c, outer border of same; d, d, tubular membrane;…
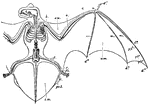
Noctule Bat
"Skeleton and volar Membranes of the Noctule Bat. c, clavicle; h, humerus; r, radius; u, ulna; d1, first…
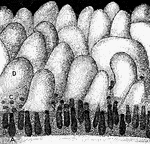
Glands and villi of the small intestine
"A, B, glands seen in vertical section with their orifices at C opening upon the membrane…

Snail
"Snail is the common name of gasteropodous mollusks. They feed chiefly on vegetable substances, though…
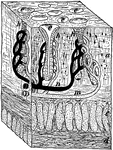
Cross-Section of Stomach Wall
"A tiny block out of the stomach wall. a, the mucous membrane; c and d, the muscles; h, gastric glands;…