Clipart tagged: ‘molar’
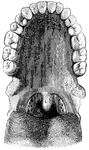
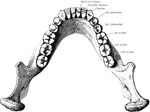
Back view of the adult mouth
"The head is represented as having been thrown back, and the tongue drawn forward. A, B…

Horse Molar
"Side view of second upper molar tooth of Anchitherium (brachyodont form)." — Encyclopedia Britannica,…
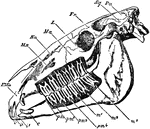
Horse Skull
"Side view of skull of horse, with the bone removed so as to expose the whole of the teeth. PMx, premaxilla;…
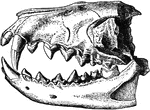
Hyaenodon Leptorhynchus
"Dentition of Hyaenodon leptorhynchus. The posterior molar is concealed behind the penultimate tooth."…
Jaw Showing Roots of Teeth
Horizontal section through both the upper and lower jaws to show the roots of the teeth. The sections…

Comparison of the Molar Teeth of a Human, Horse, and Dog
The molar teeth of a human, horse and dog. The first image to the left in a molar tooth of a horse.…
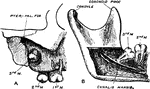
Impacted Third Molar
Impaction of the upper third molar in the maxilla. B, Impaction of the lower third molar in the mandible.
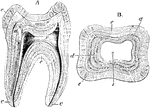
Structure of a Molar
Longitudinal section (A) and transverse section (B) of a human molar tooth. Labels: c, cement; d, dentine;…
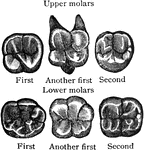
Surface of Molar
Triturating surfaces of molar teeth of right side. The upper margin of the figures corresponds to the…
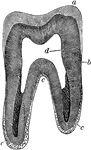
Vertical Section of a Molar
Vertical section of a molar tooth. Labels: a, enamel of the crown, the line of which indicate the arrangement…
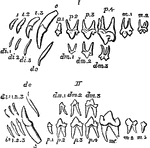
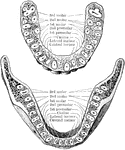
Permanent Dentition
"Milkand permanent dentition of upper (I) and lower (II) jaw of the dog, with the symbols by which the…
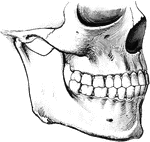
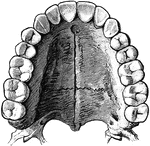
Teeth
To show the relation of the upper to the lower teeth when the mouth is closed. The manner in which a…
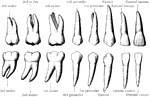
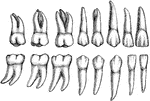
Permanent Teeth
The permanent teeth of the right side, outer or labial aspect. The upper row shows the upper teeth,…
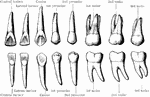
Permanent Teeth
The permanent teeth of the right side, inner of lingual aspect. The upper row shows the upper teeth,…
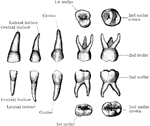
Temporary Teeth
The temporary teeth of the left side. The masticating surfaces of the tow upper molars are shown above.…
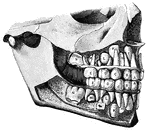
Temporary and permanent teeth
"Temporary Teeth: A, central incisors; B, lateral incisors; C, canines;…
Development of a Tooth
Diagram to illustrate the development of a tooth. I. Shows the downgrowth of the dental lamina D.L.…
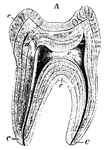
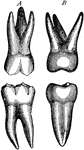
Human Tooth
A tooth is generally described as possessing a crown, neck, and root. Side view of a tooth.
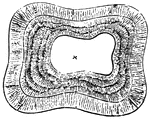
Human Tooth
A tooth is generally described as possessing a crown, neck, and root. Top view of a tooth.; 1. Central…
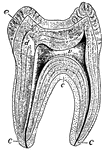
Human Tooth
A sectional view of a human molar. The roots, or fangs, are shown covered by a layer of bone called…