Clipart tagged: ‘monoclinic’
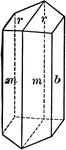
Amphibole
"Monoclinic. Crystals prismatic in habit; the prism faces make angles of 55 and 125 degrees with each…
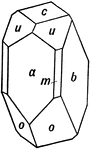
Calcium-Magnesium Metasilicate
Also known as Diopside, this crystal exhibits symbols whose forms are: (c), (b), (a), (m), (o), and…
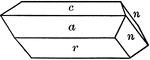
Elongation in the Direction of the Clinodiagonal Axis
In cases where the basal pinacoid is fixed by some physical property like cleavage, the elongation is…
Epidote
"Monoclinic. Crystals are often much elongated parallel to the ortho-axis with a prominent development…
Gypsum
"Monoclinic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to clinopinacoid; in diamond-shaped crystals with edges…
Gypsum
"Monoclinic. Crystals usually tabular parallel to clinopinacoid; in diamond-shaped crystals with edges…
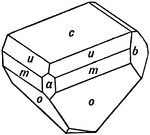
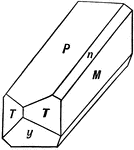
Hemihedral Crystal of Pyroxene
This image shows a hemihedral crystal of pyroxene, whose forms are (c), (b), (a), (m), (o), and (u).
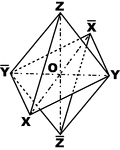
Monoclinic Axes and Hemi-pyramid
"Prisims with edges parallel to neither of the axes OX and OY...are usually called hemi-pyramids." -The…
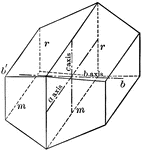
Crystal of the monoclinic system
"A crystal form does not necessarily make a solid figure. One such an example is this, of the Monoclinic…
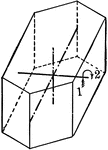
Symmetry of monoclinic system
"The symmetry of the Monoclinic System is as follows: The crystallographic axis b is an axis of binary…
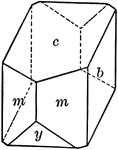
Orthoclase
"Monoclinic. Crystals are usually prismatic in habit and have as prominent forms, clinopinacoid, base,…
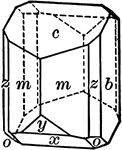
Orthoclase
"Monoclinic. Crystals are usually prismatic in habit and have as prominent forms, clinopinacoid, base,…
Stilbite
"Monoclinic. Uniform in cruciform twins. Commonly tabular parallel to clinopinacoid. Crystals usually…