Clipart tagged: ‘silicon’
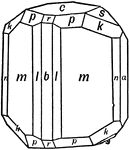
Andalusite
This figure reproduces a combination of orthorhombic forms observed on crystals of aluminum orthosilicate,…
Calamine, Hemimorphite
This figure shows a crystal of basic Zinc Silicate (calamine, hemimorphite) showing hemimorphism.
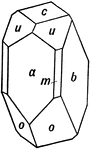
Calcium-Magnesium Metasilicate
Also known as Diopside, this crystal exhibits symbols whose forms are: (c), (b), (a), (m), (o), and…

Elongation in the Direction of the Orthogonal Axis
In some cases, the elongation of a crystal may be in the direction of the orthogonal axis, whose position…
Hypersthene
This figure exhibits a combination occurring on the ferro-magnesian meta-silicate, Hypersthene. Forms:…
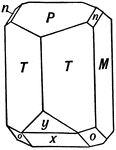
Orthoclase
This figure shows a crystal of Orthoclase, exhibiting forms (M), (P), (T), (x), (y), (o), and (n).
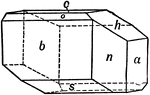
Rhodonite
This figure shows a crystal of Rhodonite (manganese meta-silicate), whose forms are: (c), (b), (a),…
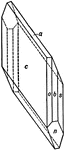
Rhodonite
An alternate combination of manganese meta-silicate (Rhodonite), showing forms: (c), (b), (a), (n),…
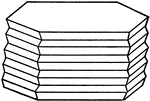
Striation of Crystal Planes
Striation of crystal planes may be produced by repeated polysynthetic twinning. This is well illustrated…