Sphaerozoum Ovodimare
"A genus compound radiolarians, typical of the family Sphaerozoidae, the protoplasm of which contains…
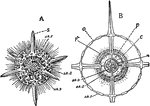
Actinomma Asteracanthion
"Actinomma Asteracanthion, a Radiolarian with a limited number of specialized radii (axes), symmetrically…

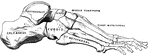
Bones of the Ankle and Foot
Bones of the Ankle and Foot. Labels: m, metatarsal bones; p, phalanges; ca, os calcis, or heel bone.

Archaeopteryx Fossil
An illustration of the skeletal fossil of Archaeopteryx, the earliest and most primitive bird known.…

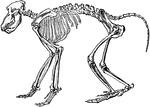
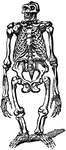
Armadillo - Endoskeleton and Exoskeleton or Dermoskeleton
An illustration of a pichiciago, a small burrowing armadillo. The front half of the animal is covered…
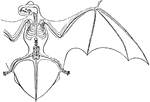
Skeleton and Wing Membranes of the Noctule Bat
The bat genus Nyctalus (Noctule bats) are Evening bats. They are distributed in the temperate and subtropical…
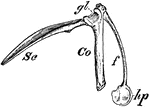
Bird Scapula
"Right shoulder-girdle or scapular arch of fowl, showing hp, the hypoclidium; f, furculum; Co, coracoid;…
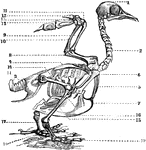
Bird Skeleton
Skeleton of a bird. 1: The head. 2: Cervical Vertebrae. 3: Dorsal and lumbar vertebrae. 4: Scapula.…
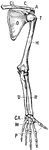
Bones of the Shoulder and Upper Extremity - Front View
"A, acromion; C, coracoid; CA, carpus; CL, clavicle; H, humerus; M, metacarpals; O, ventral surface…
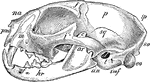
Domestic Cat Skull
"Skull of Cat (Felis catus), showing the following bones, viz. : na, nasal; pm, premaxillary; m, maxillary;…
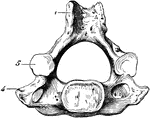
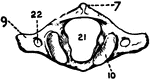
Human Cervical Vertebra Bone
A cervical vertebra of the spine, inferior surface. Labels: 1, spinous process, slightly bifid; 4, transverse…
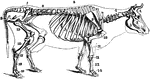
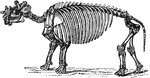
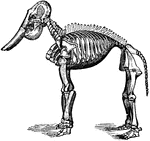
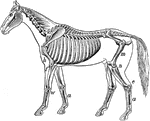
Cow Skeleton
Skeleton of the cow. 1: Frontal bone of the head. 2: Upper jaw, superior maxillary. 3: Lower jaw, inferior…

Dance of Death, The Astrologer
The Astrologer, from Hans Holbein's series of engravings, Dance of Death.
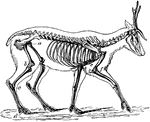
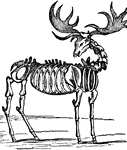
Skeleton of the Deer
"The bones in the extremities of this the fleetest of quadrupeds are inclined very obliquely towards…
Diplodocus
An illustration of a Diplodocus skeleton and the caudal vertebrae (A and B). Diplodocus is a genus of…

Dodo Skeleton
Illustration of a dodo bird skeleton. The dodo (Raphus cucullatus) was a flightless bird endemic to…
A Prehistoric Egyptian Tomb
"The skeleton lay on the left side with knees drawn up and hands raised to the head. About it were various…
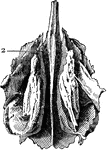
Ethmoid Bone of the Human Skull
Ethmoid bone, posterior surface. The ethmoid bone is an exceedingly light, spongy bone, placed between…
Human Femur Bone
The Femur (upper leg bone) is the longest, largest, and strongest bone in the skeleton. Labels: b, rounded…
Anterior View of Human Right Femur
"Anterior View of Human Right Femur. ec, external condyle; etu, external tuberosity; ic, internal condyle;…
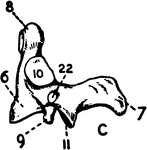
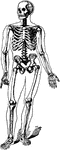
Bones of the Foot
"The foot is built in the form of a half-dome or half-arch. This is to afford a broad, strong support…
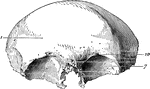
Frontal Bone of the Human Skull
Frontal bone of the human skull, outer surface. The frontal bone forms the forehead, roof of the orbital…
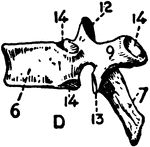
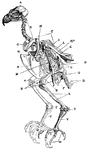
The Pelvis of a Young Grouse
"Pelvis of a young grouse, showing three distinct bones. Il,P, ilium, ischium, pubis. In front of former…
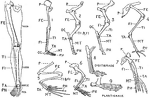
Human Leg (Front View), and Comparative Diagrams showing Modifications of the Leg
This illustration shows a human leg (front view), and comparative diagrams showing modifications of…
Humerus
"The humerus, a long, hollow bone, rests against a shallow socket on the shoulder blade. It…
Humerus
"The humerus, which moves freely by a globular head upon the scapula, forming the shoulder-joint." —…
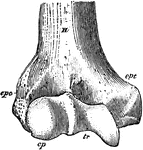
Humerus
"Anterior View, Distal End, of Right Humerus of a Man. H, humerus; epc, epicondyle, or external supracondyloid…
The Human Humerus
The human humerus bone, the longest and largest bone of the upper leg. Labels: a, rounded head; gt,…