Clipart tagged: ‘steam engine valve’
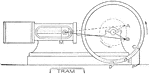
Steam Engine Valve Centered with Piston
"It is usual to put the engine on center before setting the valve. First put the engine in a position…
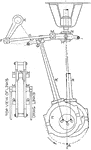
Eccentric Motion of the Steam Engine Crank in Full Gear
"When set full gear forward, the valve admits steam to the crank end of the cylinder, and the crank…
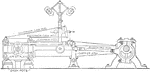
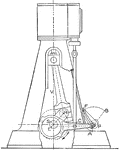
Steam Engine with Reynolds Corliss Gear
"An eccentric on the main shaft gives an oscillating motion to a circular disc called the wrist plate,…
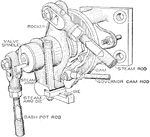
Steam Engine Brown Releasing Gear
"The governor cam rod operates a plate cam having a curved slot so shaped that it takes place of both…
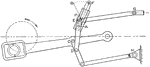
Joy Steam Engine Valve Gear Rotating Wheel
A Joy valve gear for steam engine rotating the wheel in the direction of the arrow. The lever F changes…
Outline of a Steam Engine Marshall Gear Reducing Friction and Wear
An outline of the Marshall gear from a steam engine. The piston rotates the crank shaft at point H around…
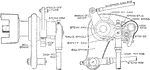
Close up of Reynolds Corliss Gear from Steam Engine
"The steam arm is keyed to the valve spindle which passes loosely through a bracket on which the bell—crank…
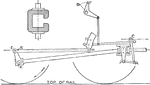
Steam Engine with Walschaert Gear on Railroad
An illustration of the steam engine with Walschaert gear system on rail tracks. The piston moves the…
Close up View of Double Sliding Valve Gears from Steam Engine
"The main valve controls admission, release, and compression; the other (valve) regulates the cut—off…
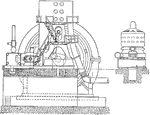
5000 kW Corliss and Curtis Steam Engine for Electric Generation
An illustration of a Corliss steam engine to generate 5000 kW of electricity. The turbines to create…
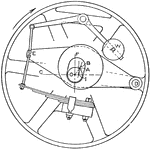
Top View of the Fly Wheel Governor Turning Clockwise
"All fly—wheel governors operate by shifting the eccentric either to change the angular advance,…
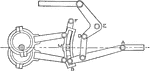
Steam Engine Gooch Link and Valve Gear Arrangement
"As the speed increases, and the link is 'notched up', the lead is increased as the cut—off is…
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Connected to Rocker
"This occurs in horizontal engines when the valve is set on top of the cylinder instead of on one side.…
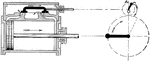
Valve with Lap of Steam Engine at Extreme Left with Exhaust Ports Open
"Since the valve must move a distance equal to the outside lap before admission can take place, it is…
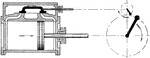
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Steam Where Slide Valve is Closed
"The relative positions of crank, eccentric and valve when the exhaust closes on the crank end and compression…
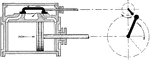
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Where Steam is Admitted to the Slide Valve
"While the crank is moving from the position, steam is being admitted to the head end and being exhausted…
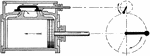
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Steam Where Slide Valve is in Open Position
An illustration of the valve with lap at the end of the crank end steam compression. The piston will…
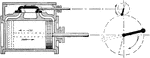
Steam Engine Valve with Lap Steam Where Slide Valve Moved to Open Position
"If the inside lap is increased, the valve must move farther before released occurs and the crank angle…
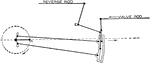
Steam Engine Rocker Arrangement with Valve and Reverse Rod in Eccentric Motion
"This arrangement makes it possible to place the valve and steam chest above the valve motion. A rod…
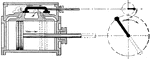
Valve with Lap of Steam Engine Where Steam Enters the Slide Valve Compartment
"The maximum displacement of the valve is attained when the eccentric is horizontal. In this position…
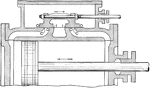
Slide Valve of Steam Engine
"The amount that the valve overlaps the steam ports is called the lap of the valve. It will at once…
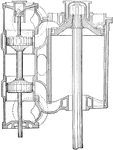
Cross Sectional View of the High Pressure Cylinder of Piston Valve from USS Massachusetts
"This valve consists of two pistons connected by a sleeve through which the valve rod passes. This valve…