Clipart tagged: ‘cannons’

Attack of the Gunboats at Fort Donelson
Attack of the gunboats at Fort Donelson, one of the most influential battles in American history. This…
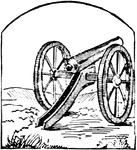
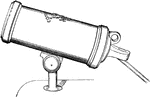
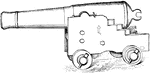
Cannon
A large hollow metal cylinder closed at one end, and variously mounted, used for throwing balls by the…

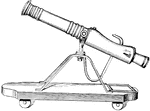
Cannon
A cannon from the time of Cortez. "It will be observed that the pieces have no trunnions, and are supported…

Constantinople
An illustration of the fortification around Constantinople and soldiers firing cannons.
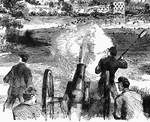
Battle at Dam No. 4
"Battle at Dam No. 4, Potomac River, between Butterfield's brigade and a large Confederate force. A…

Battle at Dam No. 4
"Battle at Dam No. 4, Potomac River, between Butterfield's brigade and a large Confederate force. A…

Battle at Dam No. 4
"Battle at Dam No. 4, Potomac River, between Butterfield's brigade and a large Confederate force. A…

Fort Runyon
"Section of Fort Runyon, Va., guarding the road to Alexandria, occupied by the Twenty-first Regiment,…

Bombardment of Fort Sumter, April 12, 1861
Confederate forces bombarding Fort Sumter on April 12, 1861

Gunboat of the Mississippi
A gunboat of the Mississippi. Gunboats Essex, Carondelete, Cincinnati, St. Louis, and Benton steamed…

Hilton Head
"Exterior view of fortifications erected by the Federal troops at Hilton Head, Port Royal. S. C. Hilton…

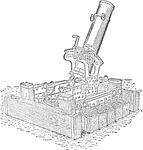
Mortar Battery Stanton
"Interior of the Mortar Battery Stanton, Tybee Island, Ga., showing the operation of 13-inch mortars…
240 mm Trench Mortar
An illustration of a 240 mm Trench Mortar used by the French during World War I, and designed by Dumezil—Batignolles.…
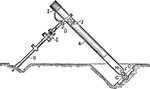
Barrel View of Stokes Mortar
An schematic illustration of the 3 inch Stokes mortar. The mortar is made out of steel and screwed onto…
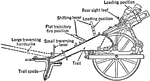
Rifled Carriage Light Minenwerfer Mortar
A light carriage minenwerfer class mortar used for direct fire. The barrel and the shifting lever is…
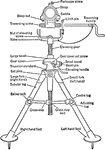
Front View of Stokes Mortar with Bipod
The illustration shows a schematic view of the Stokes Mortar being mounted onto the bipod. The mortar…
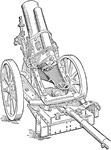
Rifled Heavy Minenwerfer Mortar
An illustration showing the German minenwerfer, or mine launcher, class for short range mortars. The…
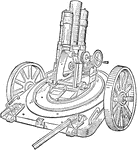
Rifled Light Minenwerfer Mortar
A light minenwerfer with 7.6 cm caliber designed by German during World War I. The series of gears adjusts…
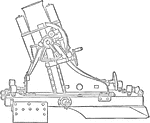
Rifled Medium Trench Mortar
The illustration of a medium trench mortar used during World War I. The mortar was designed with a rifled…
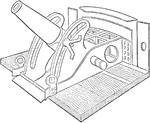
Mounted Steel Mortar
"The mortar is a stout cannon of forged steel with simple vent firing and rear trunnions. The maximum…

The Great Naval Battle on the Mississippi
First day's bombardment, Federal Schooners off Forts Jackson and St. Philip, commanding the passage…

Battle of Pittsburg Landing
Recapture of artillery by the First Ohio and other regiments under General Rousseau, April 7, 1862.…

Reconnoissance
"Reconnoissance by Colonel Max Weber's Turner rifles in the vicinity of Newmarket Bridge, on the road…
192 Pound Trench Mortar Bomb Shell
A 192 pound bomb shell for the 240 mm trench mortar used during World War I. The vanes, or wings, are…

Crossing of Shenandoah River
"Colonel Pilson's Battery shelling the rear guard of the Confederate General Jackson's Army, at the…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…

Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge
"Battle of White Oak Swamp Bridge, Monday June 30th, 1862- Ayres's, Mott's and Randall's batteries checking…