Clipart tagged: ‘crystallographic’
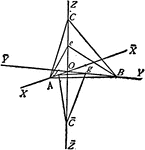
Crystallographic Axes of Reference
"...take any three edges formed by the intersection of three faces of a crystal. These axes are called…
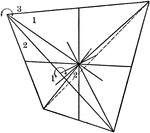
Symmetry of tetrahedral class
"The symmetry of this class is as follows: The three crystallographic axes are axes of binary symmetry;…