Clipart tagged: ‘groove’
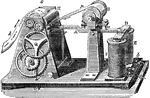
Magnetic Telegraph
"Morse magnetic telegraph will be understood by reference to the accompanying diagram, which represents…
!["[The pulley] consists of a wheel with a grooved circumference, over which a rope passes, and an axis or pin, round which the wheel may be made to turn. A represents the block, B the axis, C the wheel." —Quackenbos 1859](https://etc.usf.edu/clipart/36300/36348/pulley_36348_mth.gif)
Pulley
"[The pulley] consists of a wheel with a grooved circumference, over which a rope passes, and an axis…

Pulley
A pulley (also called a block) is a mechanism composed of a wheel (called a sheave) with a groove between…
Pulley
A pulley (also called a block) is a mechanism composed of a wheel (called a sheave) with a groove between…

Pulley Blocks
An illustration of a block pulley. A pulley (also called a block) is a mechanism composed of a wheel…
Pulley Blocks
An illustration of a block pulley. A pulley (also called a block) is a mechanism composed of a wheel…
Pulley Blocks
An illustration of a block pulley. A pulley (also called a block) is a mechanism composed of a wheel…
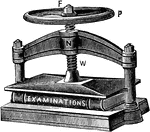
Screw press
"A screw is a cylinder, generally made of wood or metal, with a spiral ridge (the thread) winding about…
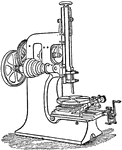
Slotting Machine
"The slotting machine also cuts grooves and slots, but in an entirely different manner. Those who are…
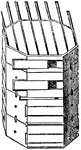
Stewarton Hive
"A hive largely and successfully used in Scotland, it is octagonal, and the "Quinby hive" of America…
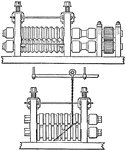
Two-high Trains
"Two kinds of successions of grooves used for rectangular bars in "two-high" train." — The Encyclopedia…