Clipart tagged: ‘manometer’
Compressed Air Manometer
"The compressed air manometer consists of a strong graduated glass tube of uniform narrow bore, closed…
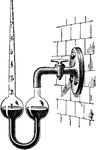
Compressed Air Manometer
This instrument consists of a bent tube closed at one end and containing within the space a quantity…
McLeod Gauge
A McLeod gauge isolates a sample of gas and compresses it in a modified mercury manometer until the…
McLeod Gauge
A McLeod gauge isolates a sample of gas and compresses it in a modified mercury manometer until the…
Vacuum Gauge
A vacuum gauge is used to measure the pressure in a vacuum — which is further divided into two…
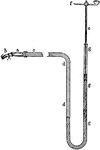
Manometer
"Mercury manometer for recording blood-pressure. d g, glass U-tube partly filled with mercury. In one…
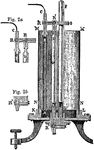
Regnaults Manometer
"AB is a strong metal tube, closed at the lower end, and carrying at the upper a bent pipe for admitting…
